
Living organisms consist of two fundamentally different cells types: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotes (organisms consisting of prokaryote cell types) include the bacteria (heterotrophic nutrition) and cyanobacteria (autotrophic nutrition). Eukaryotes (organisms consisting of eukaryote cell types) include all other living forms of life which you are familiar such as: amoeba, paramecium, mosses, fungi, plants and animals. Eukaryote cells can further be classified as plant cell types, animal cell types and fungi cell types.
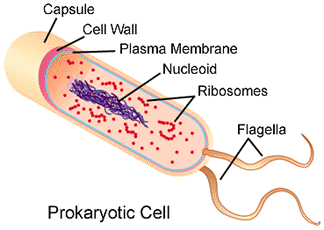
Study behavioral objective 14 and read the pages indicated by B-18. Prokaryotic cells are much smaller (less than 5 micrometers) than eukaryotic cells (5 millimeters to 100 centimeters). Most prokaryotic cells are surrounded by a cell wall (noncellulose) with a relatively simple internal structure (lacking most membrane bound organelles). The structures included in a prokaryote cell are: cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm containing ribosomes, DNA in circular form lacking a membrane surrounding located in a region called the nucleoid region, a few have flagella. In your notes draw a figure of a prokaryote and eukaryote cell. Write a paragraph comparing and contrasting these two cell types and make table listing these differences (include cell membrane, mitochondria, chloroplast, ER, Golgi, lysosomes, nucleolus, DNA form, nuclear membrane, ribosomes, cell wall, flagella) .
Place the table below in your notes with the correct answers.
| STRUCTURES | PROKARYOTE
present/absent : differences |
EUKARYOTE
present/absent : differences |
| cell wall | ||
| cell membrane | ||
| chromosomes | ||
| nucleus | ||
| nuclear membrane | ||
| nucleolus | ||
| mitochondria | ||
| chloroplast | ||
| ribosomes | ||
| endoplasmic reticulum | ||
| Golgi Body | ||
| lysosome | ||
| large vacuole | ||
| cytoskeleton | ||
| centrioles | ||
| leucoplasts |
Place the table below in your notes with the correct answers.
| STRUCTURES | PLANT CELL
present/absent |
ANIMAL CELL
present/absent |
| cell wall | ||
| cell membrane | ||
| chromosomes | ||
| nucleus | ||
| nuclear membrane | ||
| nucleolus | ||
| mitochondria | ||
| chloroplasts | ||
| ribosomes | ||
| endoplasmic reticulum | ||
| Golgi Body | ||
| lysosomes | ||
| large vacuole | ||
| cytoskeleton | ||
| centrioles | ||
| leucoplasts |
14. Describe differences between plant and animal cells.
Press here to check answer. press
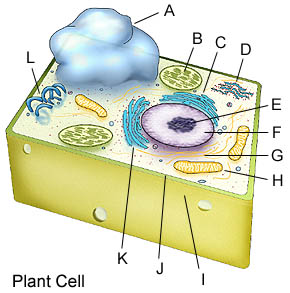
15. Identify those structures found in plant cells but not animal cells.
Press here to check answer. press
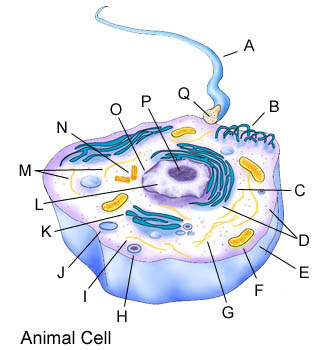
16. Identify those structures found in animal cells but not plant cells.
Press here to check answer. press
17. Which of the following cell structures are found in prokaryote, eukaryote (plant), and eukaryote (animal) cells?
a) plastid, mitochondrion, Golgi body, nucleus
b) ribosomes, DNA,
c) chloroplast, cell wall
d) mitochondria, lysosome, cell wall
Press here to check answer. press
18. Which of the following cell structures are found in eukaryote
(plant), but not in eukaryote (animal) cells?
a) plastid, mitochondrion, Golgi body, nucleus
b) ribosomes, DNA,
c) chloroplast, cell wall
d) mitochondria, lysosome, cell wall
Press here to check answer. press
19. Which of the following cell structures are not found in eukaryote
(plant), but are found in eukaryote (animal) cells?
a) Golgi body
b) ribosomes, DNA,
c) chloroplast, cell wall
d) centrioles
Press here to check answer. press
20. Which of the following cell structures are found in prokaryote
but not in eukaryote (plant), and eukaryote (animal) cells?
a) single circular DNA molecule
b) many linear DNA molecules
c) ribosomes
d) cell wall
Press here to check answer. press
21. Which of the following have ribosomes and circular DNA?
a) prokaryote cells only
b) eukaryote cells only
c) prokaryote cells, mitochondria, chloroplast
d) eukaryote cells, lysosome, Golgi bodies
Press here to check answer. press
Read the pages and study figures indicated by B- 18 concerning
examples of prokaryote cells, eukaryote plant cells and eukaryote animal
cells.
This is the end of lesson four. Click here to go back to the
Biology 109N home page and to lesson five. Transport Across the Membrane.
click
For information on how to use this page, go to How
to Use This Site.
Created by the Center for Learning Technologies, Academic Technology Services.
Last modified October 22, 1997.