
In miniunit Beta you learned the various organelles which may be found
in cells,
their function and structure. In miniunit Gamma you are going to learn
how cells
and their organelles reproduce. The perpetuation of life is based on
the reproduction of cells. In eukaryotic cells the organelles chloroplasts
and mitochondria must also be able to replicate. The other organelles (ribosomes,
golgi, endoplasmic reticulum, etc.) are synthesized by the newly formed
cell. In miniunit Beta you learned that cells may be classified as eukaryote
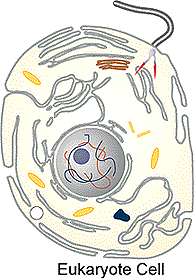
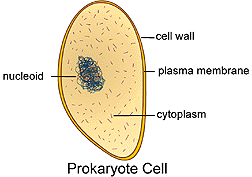
or prokaryote (see above figures) . Both of these cell types along with
the organelles chloroplasts and mitochondria contain DNA molecules. The
cell's total hereditary endowment of DNA is called its genome which consists
of one or more DNA molecules. Arranged along the length of each DNA molecule
are thousands of genes the hereditary units that determine an organism's
traits. Cell division includes two processes: distribution of identical
genetic material located on DNA molecules to two newly formed daughter
cells and the separation of of the cytoplasm into two parts called cytokinesis.
Most of the behavioral objectives in this miniunit will be concerned with
cellular reproduction of eukaryotic cells; however, you will also learn
how prokaryotic cells and two of the cells organelles (chloroplasts and
mitochondria) reproduce. At this time you may want to go back to miniunit
Beta and restudy the following cell types and organelles - eukaryote,
prokaryote, chloroplast, mitochondrion.
Read the pages indicated by G-1 in the text and study behavioral objectives 17 and 18. Write a paragraph describing the two cell types and organelles identified above.
The types of division which will be examined in this miniunit are :
binary fission - asexual reproduction by dividing the body cell in half forming two identical cells with the same genome. This type of division occurs in the prokaryote cells and the organelles chloroplast and mitochondrion.
mitosis - asexual reproduction in eukaryote cells where the nucleus divides in an orderly process forming two nuclei with genetically identical genomes followed by the division of the cytoplasm so that each daughter cell receives one of these nuclei.
meiosis - type of cell division which occurs in organisms consisting of eukaryotic cells where the nucleus divides in an orderly process forming four cells with nuclei that contain only one half of the the number of DNA molecules. During the process a diploid cell will divides twice to form four haploid cells. This type of cell division occurs prior to the formation of sex cells (gametes) which will fuse together during fertilization forming a zygote.
1. Read the descriptions concerning prokaryote and eukaryote cell type below and indicate which cell type the description best fits.
A. prokaryote cell type
B. eukaryote cell type
1. Extremely small cells containing only a few organelles.
2. Nuclear membrane surrounding the chromosomes (condensed
DNA
molecules).
3. Contains many membrane cell organelles such as chloroplasts
and mitochondria.
4. Bacteria and cyanobacteria are organisms consisting
of this cell type.
5. Plants and animals consists of this cell type.
1
2
3
4
5
a)
A A
B
B
A
b)
B B
A
B
B
c)
A B
B
B
A
d)
A B
B
A
B
Press here to see correct answer. press
k
2. In the cell above where is the genome located?
- a) cytoplasm
- b) nucleoid
- c) cell wall
- d) a and c
k
3. In the cell above which process will be used during cellular reproduction?
- a) mitosis
- c) meiosis
- b) binary fission
- d) a and b
Answer the two questions concerning the figure below.

4. In the figure above identify the red and blue linear structures.
- a) mitochondria
- c) DNA in form of chromosomes
- b) vacuoles
- d) endoplasmic reticulum
- a) mitosis
- b) meiosis
- c) binary fission
- d) a and b

6. Identify the four yellow oblong structures and indicate which process is used during their replication.
- a) nucleus - mitosis
- b) golgi - meiosis
- c) centriole - binary fission
- d) mitochondria - binary fission
In your notes draw pictures of these two cell types (prokaryote and
eukaryote) and the two organelles (mitochondrion and chloroplast). Identify
the parts: DNA (circular and linear threads), nucleus, cell membrane, nucleoid,
cytoplasm, membrane matrix in both cell types and organelles.
Click here to review these cell types and the
organelles chloroplast and mitochondrion.
For information on how to use this page, go to How
to Use This Site.
Created by the Center for Learning Technologies, Academic Technology Services.
Last modified October 22, 1997.