animal life cycle 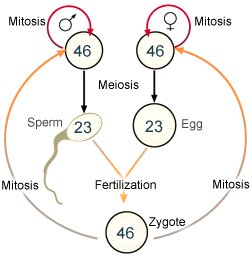
Read the pages indicated by G-9 and study behavioral objectives 19, 20 and 21. Study the figure above which represents the human life cycle. In human somatic cells there are 23 pair of homologous chromosomes (total of 46 chromosomes). If two somatic cells combined during fertilization the cell formed would have 92 chromosomes and with every new generation their would be a doubling of chromosomes compared to the parent. This does not occur. You have the same number of chromosomes as your parents and your children. In order for two cells to combine and contain the same number of chromosomes as the parents the two cells must reduce their chromosome number by one half.
note: meiosis
In humans you would start out with 46 somatic cell chromosomes
in both parents. The sex cells (egg and sperm) will form with only
23 chromosomes per cell. During fertilization these two cells will
combine to form a zygote with 46 chromosomes. The process where
cells with only one half the number of chromosomes are formed
is called meiosis. This reduction process is not random.
You learned earlier that diploid cells contain homologous pair of chromosomes.
During meiosis each new cell formed will receive only one of each homologous
pair of chromosomes. During fertilization one chromosome of each
homologous pair from each parent will combine by fertilization to
form a diploid (pairs of homologous chromosomes)
zygote which divides by mitosis to develop into an embryo and eventually
an adult. Draw this cycle in your notes and identify the various parts.
results of meiosis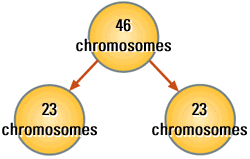
The figure above shows the results of meiosis in humans. The somatic
mother cell contains 46 chromosomes (top). The newly formed cells contain
23 chromosomes. These cells are haploid because they contain one
of each homologous pair of chromosomes.
7. Draw two cells - one containing 3 homologous pair of chromosomes
(diploid) and the second showing the chromosome compliment after meiosis
forming a cell with one of each homologous pair (haploid).
Press here to check answer. press
B
C
8. Which cell(s) represent(s) a haploid compliment of chromosomes?
a) A
b) B
c) C
Press here to check answer. press
9. Where does meiosis occur in humans?
a) all somatic cells b) selected
cells in the testis or ovaries
Press here to check answer. press
Examine the figure depicting the human life cycle and
answer the questions below.
cycle
10. The sperm cell is: diploid or haploid.
Press here to check answer. press
11. The zygote is : diploid or haploid
Press here to check answer. press
12 Another name for the sperm and egg cells:
a) gametes b) somatic body cell
Press here to check answer. press
This is the end of lesson four. In lesson five, Eukaryotic Cell
Cycle - Meiosis, you will learn the different steps involved
during meiosis. Cell division which reduces the chromosomes
by one half.
Click here. click
For information on how to use this page, go to How
to Use This Site.
Created by the Center for Learning Technologies, Academic Technology Services.
Last modified October 22, 1997.