


Next: About this document ...
to Name: Honor Code Signature:
Physics 101 Final Exam
8 Dec 2003
Prof L. Weinstein
There are 34 questions. Unless otherwise noted, please give a short
explanation for all of your non-numerical answers. Show your work for
all numerical answers.
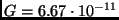 N
N m
m /kg
/kg
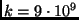 N
N m
m /C
/C
Earth's mass
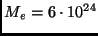 kg
kg
Earth's radius
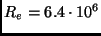 m
m
Moon's mass
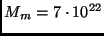 kg
kg
Moon's radius
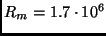 m
m
Earth-Moon distance
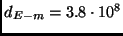 m
m
Earth-Sun distance
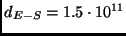 m
m
I am not allowed to use any part of your SSN to publicly post grades
or other private information without your permission.
Check here to let me use the last four digits of your
student ID number to post your exam, homework, and lab grades on the
web.
Alternatively, write a five digit number here for me
to use to post your exam, homework, and lab grades on the web.
- If two electrons initially at rest are placed close to each
other they will exert a force on each other. Ignore all other forces.
When the electrons are released and are free to move, they will move
- further away from each other
- not at all (they will not move)
- closer to each other
- Need more information
- In the previous problem, when the electrons are released and
start moving, the force on each will
- increase as they move
- decrease as they move
- remain constant as they move
- Nonsense, they won't move
- Need more information
- (no explanation needed) You electrically polarize a neutral
metal sphere. This means that
- the sphere is now electrically charged
- some positive charges are on one side of the sphere and an equal
number of negative charges are on the other side
- it is now an insulator
- it is magnetic
- Need more information
- (No explanation needed) I have two 100-g copper rods. I
stretch one so that it is
10 cm long and about 1 cm in diameter. I stretch the other one so that it
is 100 cm long and about 0.3 cm diameter. Which one has more resistance?
- the 10 cm long rod
- the 100 cm long rod
- both are the same
- Need more information
- A 32-inch television set has about a 5000 V difference between the
back of the set and the screen. The distance between the back of the
TV set and the screen is 0.6 m. If 3 mC of electrons travel from the
back of the set to the screen, how much kinetic energy do they gain?
- A 6-Volt battery is connected to a 3-
 light bulb. What
is the current flowing through the circuit?
light bulb. What
is the current flowing through the circuit?
- How much electrical power does the light bulb in the previous
problem use?
- If you double the voltage of the battery in the previous
problem, what happens to the current in the circuit?
- it quarters
- it halves
- it does not change
- it doubles
- it quadruples
- Need more information
- A pair of light bulbs connected in parallel to a battery will draw
- more current than a single bulb would draw
- less current than a single bulb would draw
- the same current that a single bulb would draw
- Need more information
- As you increase the number of identical light bulbs in this
circuit from 1 to 2 to 3 as shown,
the total power used by the circuit (if it is plugged into a 120-V AC wall outlet)
= 1.5in
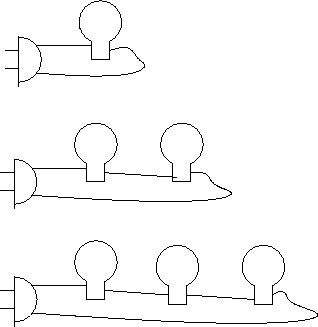
- increases
- decreases
- remains the same
- Need more information
- (no explanation needed) A moving electric charge will always
interact with (ie: have a force
exerted on it by)
- a constant electric field
- a constant magnetic field
- both
- neither
- Need more information
- (No explanation needed) Like kinds of magnetic poles repel.
Unlike kinds of magnetic poles
- attract
- repel
- either attract or repel
- Need more information
- A beam of electrons is travelling toward the East. If I want
to deflect the beam so it travels toward the north-east, then I should apply a
force pointing
= 1.5in
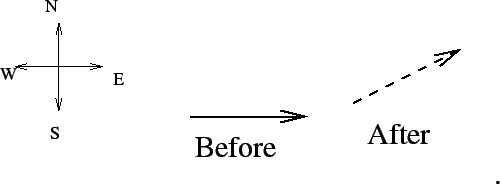
- North
- East
- Up
- West
- other
- Need more information
- A beam of electrons is travelling from East to West. If I want
to apply a southward force, then I should apply a
magnetic field pointing
= 1.5in
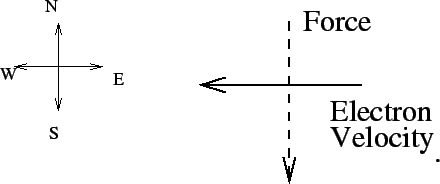
- North or South
- East or West
- Up or down (ie: into or out of the page)
- nonsense, a magnetic field won't deflect the electron beam
- Need more information
- My particle detector needs about 12,000 V but only about 20 W to
operate. I have a transformer with 50 turns in the primary coil. I
connect the primary coil to a 120-V AC outlet and the secondary coil
to my detector. How many turns does the transformer need to have in
its secondary coil to supply 12,000 V to my detector?
- I make an electromagnet by winding an insulated wire around a
hollow plastic tube. If I put 3 A of current through the wire, then
the electromagnet can pick up two paperclips. Now I place an iron rod
inside the plastic tube. How many paperclips can the electromagnet
pick up now?
= 1.5in
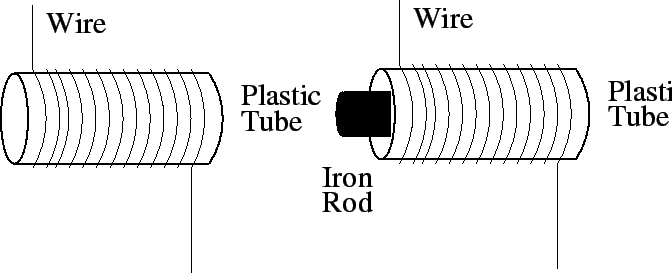
- less than 2
- 2
- more than 2
- Need more information
- You do an experiment in outer space far away from the pesky
effects of gravity and friction. A 0.2-kg bar magnet is launched
horizontally from left to right at a speed of 4 m/s through a 0.5 m
long stationary aluminum pipe with a mass of 1 kg. What is the
speed of the magnet after it exits the pipe?
= 1.in
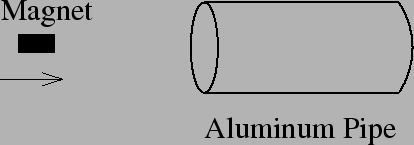
- less than 4 m/s
- 4 m/s
- more than 4 m/s
- Need more information
- In the previous problem, in what direction is the pipe moving
after the magnet exits the pipe?
- to the left (opposite the direction of the magnet)
- to the right (in the same direction as the magnet)
- nonsense, the pipe is not moving
- Need more information
- (no explanation needed) I use a bar magnet to pick up a small
iron rod. This temporarily magnetizes the rod. Which diagram
indicates the magnetic orientation of the rod?
= 1.in
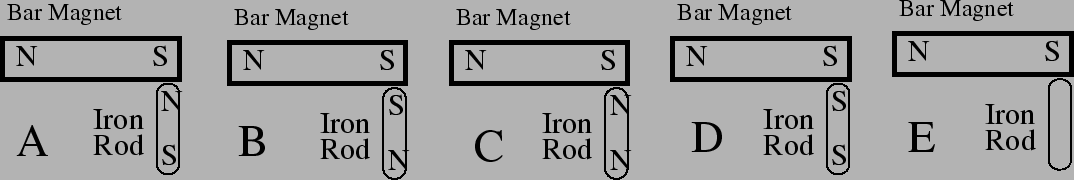
- N on top, S on bottom
- S on top, N on bottom
- N on top, N on bottom
- S on top, S on bottom
- it is not magnetized at all
- Need more information
- A large wheel is free to rotate around its hub. Three ropes are
attached to three points on the wheel. You can pull on any one rope
with a certain force for a very short time (same force and time on
each rope). Which rope should you pull on in order to exert the
maximum torque on the wheel? (You cannot change the direction of the
rope.)
= 1.in
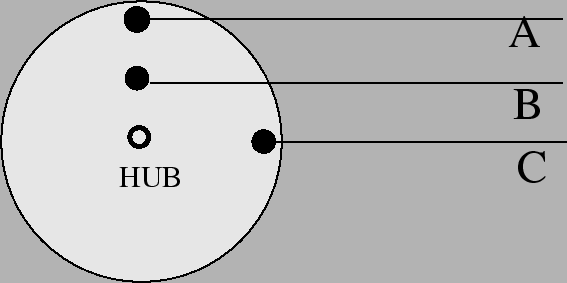
- rope A
- rope B
- rope C
- rope A or C
- Need more information
- The wheel shown below has a mass of 30 kg. I add a
5-kg block to the wheel. Where should I add the block in order to
maximize the rotational inertia of the wheel plus block?
= 1.in
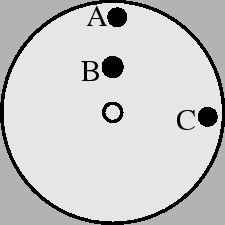
- point A
- point B
- point C
- points A or C
- Need more information
- A ball slides down a curved frictionless slope as shown in the figure. At
which point does the ball have the greatest acceleration?
= 1.in
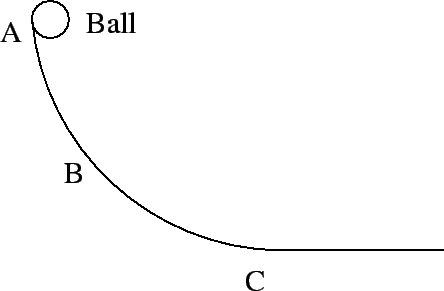
- point A
- point B
- point C
- all the same
- Need more information
- A ball slides rolls down a curved frictionless slope as shown in the
previous problem. At which point does the ball have the greatest
speed?
- point A
- point B
- point C
- all the same
- Need more information
- Dave's pickup truck has rear-wheel drive. In order to improve
traction in the snow, Dave put three fifty-pound sandbags in the back
of the pickup truck over the rear wheels. The sandbags are not tied
down. If the pickup truck stops VERY suddenly, where will the
sandbags end up?
- They will move backwards (relative to the pickup) and fall off
the rear of the pickup truck
- They will stay where they are in the pickup truck
- They will move forwards (relative to the pickup) and slam into
the cabin (front) of the pickup truck
- Need more information
- An 5-kg object is sliding in a straight line along the surface
of an icy pond at a constant 13 m/s. What is the net force on the
object?
- A proton (mass = 1 amu) travelling at
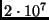 m/s hits a
neutron of the same mass. They stick together to form a deuterium
nucleus.
m/s hits a
neutron of the same mass. They stick together to form a deuterium
nucleus.
- What is their total momentum before the collision? (Hint:
use `amu' for the mass units instead of kg.)
- What is the speed of the deuterium nucleus (ie: the proton and
neutron stuck together) after the collision?
- Suppose that there is another planet named `Dirt' that is the
same size as the Earth but with only half the mass. The
gravitational acceleration
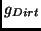 on the surface of Dirt will be
on the surface of Dirt will be
- 1/4 that of Earth
- 1/2 that of Earth
- the same as Earth
- twice that of Earth
- four times that of Earth
- Need more information
- A satellite in orbit 200 km above the Earth needs a speed of
8 km/s to stay in orbit. A satellite in orbit around Dirt will
need a speed of
- less than 8 km/s
- 8 km/s
- more than 8 km/s
- Need more information
- A satellite is in orbit around the Earth at a height of 200 km
(6600 km from the center of the Earth). It has a tangential speed of
8 km/s. How much time does it take to complete one orbit around the Earth?
- A gallon of gasoline contains about
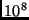 J of chemical
energy. If we could convert that chemical energy to kinetic energy
with 100% efficiency, what speed would your 2000 kg car be going
(ignore friction and air resistance)? Give your answer in m/s and
then connvert it to mph using 1 m/s
J of chemical
energy. If we could convert that chemical energy to kinetic energy
with 100% efficiency, what speed would your 2000 kg car be going
(ignore friction and air resistance)? Give your answer in m/s and
then connvert it to mph using 1 m/s 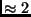 mph. Is this a lot?
mph. Is this a lot?
- You raise a textbook of mass
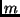 to certain height, giving it a
certain amount of potential energy. If you now raise a second textbook of
twice the mass to the same height, its potential energy will be
to certain height, giving it a
certain amount of potential energy. If you now raise a second textbook of
twice the mass to the same height, its potential energy will be
- 1/4 as much
- 1/2 as much
- the same
- twice as much
- four times as much
- Need more information
- Two charged objects that are free to move are separated by a
distance of 10 m. Object
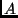 has a mass
has a mass 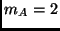 kg and a charge
kg and a charge
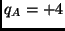 mC. Object
mC. Object 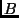 has a mass
has a mass 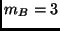 kg and a charge
kg and a charge 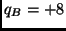 mC. What is the electrical force acting on object
mC. What is the electrical force acting on object 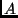 ?
?
- In the previous problem, what is
the electrical force acting on object
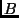 ?
?
- In the previous problem, what is the acceleration of object
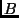 ?
?



Next: About this document ...
2003-12-10
![]() N
N![]() m
m![]() /kg
/kg![]()
![]() N
N![]() m
m![]() /C
/C![]()
![]() kg
kg
![]() m
m
![]() kg
kg
![]() m
m
![]() m
m
![]() m
m








