Next: About this document ...
to Name: Honor Code Signature:
Physics 102 Final Exam
6 May 2002
Prof L. Weinstein
There are 34 questions. Unless otherwise noted, please give a short
explanation for all of your non-numerical answers. Show your work for
all numerical answers.
I am not allowed to use any part of your SSN to publicly post grades
or other private information without your permission.
Check here to let me use the last four digits of your
student ID number to post your exam, homework, and lab grades on the
web.
Alternatively, write a five digit number here for me
to use to post your exam, homework, and lab grades on the web.
- Two different objects have the same momentum. Do they have to have
the same velocity?
- yes
- no
- need more information
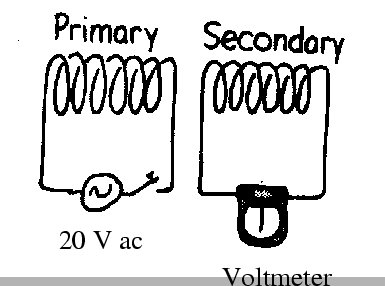
- The primary coil of a step-up transformer has 100 turns and
draws 100 W at 20 V. The secondary coil of the transformer has 10,000 turns.
How much voltage does the secondary coil provide?
- A big battery is connected to a lamp by means of a transformer.
When the switch is pressed down and held closed for 5 minutes will the
lamp stay lit for the entire time?
= 2.2in
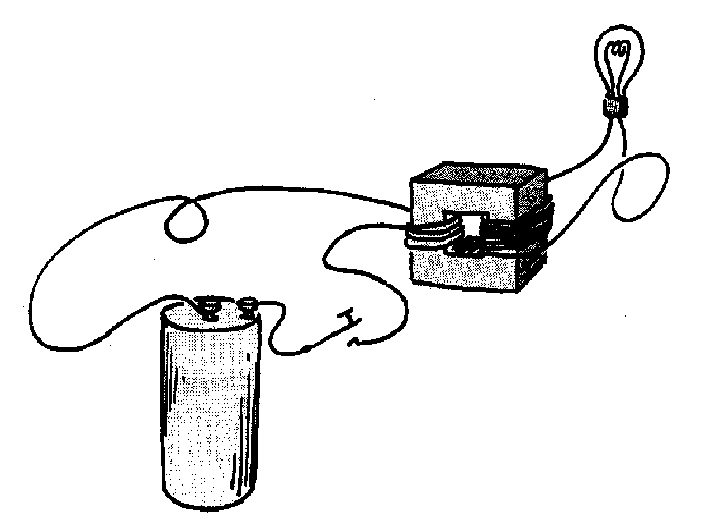
- Yes, if the battery is powerful enough.
- No.
- Need more information.
- Electric railroad locomotives in the mountains use electric
motors to turn their wheels when they go uphill. When they go
downhill, is it possible to use the electric motor
to slow them down (ie: as a brake)? Explain.
- yes
- no
- need more information
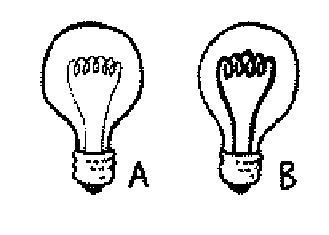
- Light bulbs A and B are identical in all ways except that B's
filament is thicker than A's. Which bulb has more resistance?
= 1.2in
- A
- B
- both the same
- need more information
- Light bulbs A and B are identical in all ways except that B's
filament is thicker than A's. If screwed into 110-volt sockets, which
bulb will be brightest?
- A
- B
- both the same
- need more information
- When I dropped a bar magnet through a vertical length of pipe in
class, the bar magnet dropped VERY slowly because of magnetic
induction. After the first half-second, it is moving at constant
downward velocity. If the mass of the bar magnet is 0.15 kg and the
mass of the pipe is 2 kg, what is the force exerted on the bar magnet
by the pipe after the first half-second?
= 1.5in
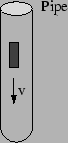
- The space shuttle is in a circular orbit around the Earth
travelling at 8 km/s. It can generate electrical power by induction by
dragging a long wire through the Earth's magnetic field. It can then
use this electrical power to operate its lights, computers, motors,
etc. If the space shuttle does this, what will happen to its orbit?
= 1.2in
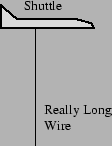
- It will lose kinetic energy, slow down, and eventually hit the Earth.
- Its kinetic energy will not change and its orbit will not change.
- It will gain kinetic energy, speed up, and move further from the Earth.
- Need more information.
- I push a 0.2 kg bar magnet through a 250-turn, 3-kg coil of
wire. It induces a current in the coil. If the coil exerts 2 N of
force on the bar magnet, what force does the bar magnet exert on the
coil?
- A 2000 kg truck travelling at 30 m/s (about 65 mph) hits a
stationary 1000 kg car. They stick together.
= 1.2in
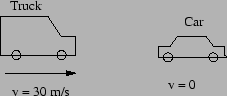
a) What is the total momentum of the truck plus car before the collision?
b) What is the total momentum of the truck plus car after the collision?
c) What is the speed of the truck plus car after the collision?
d) What is the total kinetic energy of the truck plus car before the
collision? (Use scientific notation.)
e) What is the total kinetic energy of the truck plus car after the
collision? (Use scientific notation.)
- An AC power supply is connected to a switch and a coil. An
adjacent coil is connected to a voltmeter. When the switch is closed,
the voltmeter reads 2 V. If an unmagnetized iron rod is inserted
through both coils and left there, the voltmeter will read
= 1.5in
- 0 V
- between 0 and 2 V
- 2 V
- more than 2 V
- need more information
- (No explanation needed) Two long parallel wires,
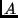 and
and 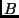 ,
are separated by 3 cm. They each carry a current of 5 A. What forces
do they exert on each other (circle all that apply)?
,
are separated by 3 cm. They each carry a current of 5 A. What forces
do they exert on each other (circle all that apply)?
= 1.1in
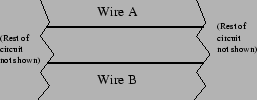
- gravitational
- magnetic
- electrical
- friction
- tension
- Can an electron at rest in a constant magnetic field be made to
move by the magnetic field?
- Yes
- No
- An electron is at rest. Can it be made to move by a changing
magnetic field?
- Yes
- No
- (no explanation needed) A wire placed in a region of constant
magnetic field has a 20 A current through it. The magnetic field goes
from left to right and the current in the wire goes from down to up
(see figure). What direction is the force on the wire?
= 1.2in
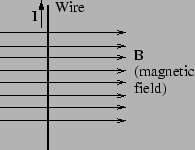
- into or out of the page
- left or right
- up or down
- other
- need more information
- (no explanation needed) A bar magnet has a north pole and a
south pole. I break the magnet in half. I now have
- one north pole magnet and one south pole magnet
- two smaller bar magnets, each with a north and a south pole
- one magnet and one piece of unmagnetized iron
- other
- need more information
- The wires in a circuit in my house can carry 20 A without
overheating. The voltage is 110 V. My favorite lightbulb has 55
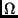 .
.
a) How much current does one light bulb draw?
b) How many light bulbs can I connect in parallel to this circuit
without overheating the wires?
- I have an ideal 1.5 V battery (ie: a battery that can deliver
as much current as I want at 1.5 V) and fifteen 3-
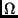 light
bulbs. How many light bulbs should I connect in series to get the
maximum amount of light?
light
bulbs. How many light bulbs should I connect in series to get the
maximum amount of light?
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 15
- need more information
- I paid the electric company $100 last month. They charge
$0.10 per kiloWatt-hour. How many electrons did they send me that I
got to keep? (Hint: your answer should be in Coulombs, not kW-hr.)
- The electric field of the Earth is 100 N/C at the Earth's
surface and points downward. George has a mass of 80 kg.
a) What is George's weight?
b) How much electric charge would have to be added to George so that
the force from the Earth's electric field balanced his weight (ie: so
he could fly)?
- Two charged metal spheres are 3.9 m apart. If the distance
between them doubles, then the electric force between them
- quadruples
- doubles
- is unchanged
- halves
- quarters
- need more information
- Two charged metal spheres are 3.9 m apart. If the distance
between them doubles, then the gravitational force between them
- quadruples
- doubles
- is unchanged
- halves
- quarters
- need more information
- When I was zapped by a spark from the van de Graaf generator I
did not die because
- the spark had high voltage but low current
- the spark had high current but low voltage
- the spark had low current and low voltage
- I did die but they forgot to put a wooden stake in my heart
- other
- How much energy does 1 microCoulomb of charge gain when it
passes through a 50,000 V potential difference?
- Hepzibah is on a new planet. In order to determine the
acceleration of gravity she drops a rock from a height of 30 m.
It takes 3 s to fall.
a) What is the average speed of the rock during its fall?
b) What is the acceleration of the rock during its fall? (Hint:
average speed is not instantaneous speed.)
- Early bicycles had a huge front wheel, often as tall as a
person. Which has more rotational inertia, a 5 kg wheel with a large
radius (eg: 1 m) or a 5 kg wheel with a smaller radius (eg: 0.5 m)?
- the larger wheel
- both the same
- the smaller wheel
- need more information
- The gravitational acceleration at the Moon's surface is about
1.6 m/s
 . Let's say that you can apply a maximum force of 400 N
(about 90 lbs).
. Let's say that you can apply a maximum force of 400 N
(about 90 lbs).
a) If you apply your force vertically, could you lift a 50 kg block on
the Moon? Could you lift it on Earth?
b) If you apply your force horizontally, what acceleration would the
block have on the moon (ignore friction)?
- The hang time of a basketball player who jumps a vertical
distance of 2 feet (0.6 m) is about 2/3 of a second. What will be the
hang time if the player reaches the same height while jumping 4 feet
(1.2 m) horizontally?
- less than 2/3 s
- the same (ie: 2/3 s)
- more than 2/3 s
- need more information
- (no explanation needed) I can accumulate a net negative charge
on myself in the winter by scuffing my feet on a wool carpet. If I do
this, then the carpet becomes
- less positively charged
- equally positively charged
- more positively charged
- negatively charged
- need more information
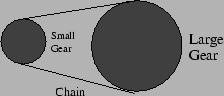
- A bicycle has one (or more) large gears attached to the pedals
and one (or more) smaller gears attached to the back wheel. The two
gears are connected by a chain. The front gear has a radius of 6 cm
and the rear gear has a radius of 3 cm. The bicyclist pedals so that
the front gear makes one revolution per second.
How many revolutions per second does the rear gear (and hence the
rear wheel) make?
= 1.in
- In the previous problem, if the bicyclist wants to go faster
without pedalling faster, she should use a
- smaller rear gear
- same size rear gear
- larger rear gear
- the rear gear size does not change the bike's speed
- need more information
- A child dropped his marbles on the floor of the school bus when
it was stopped at a traffic light. When the bus accelerates forward,
the marbles
- roll toward the back of the bus
- stay where they are
- roll toward the front of the bus
- need more information
- My 1000 kg car can decelerate (ie: brake) at 3 m/s
 . If I am
driving at 15 m/s (about 30 mph), I can stop my car in a distance of
37.5 m. If I am driving at 30 m/s (about 60 mph), then the distance
I need to stop my car
. If I am
driving at 15 m/s (about 30 mph), I can stop my car in a distance of
37.5 m. If I am driving at 30 m/s (about 60 mph), then the distance
I need to stop my car
- decreases
- stays the same
- doubles
- quadruples
- need more information
- If you think of the Earth as a giant magnet, then the North
Pole of the Earth is actually
= 1.2in
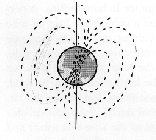
- the south pole of the magnet
- the north pole of the magnet
- the east pole of the magnet
- other



Next: About this document ...
2003-12-02