


Next: About this document ...
to Name: Honor Code Signature:
Physics 101 Exam 1
6 October 2003
Prof L. Weinstein
There are 19 problems. Please give a short explanation for all
multiple choice questions. Show your work for all numerical answers.
- A force of 12 N acts on a 2-kg block for 3 s. What is the
acceleration of the block during that time?
- A 3-kg car travelling at 30 m/s East stops gradually in 6 s. What is
the acceleration of the car (give magnitude and direction)?
- Two trains are running on parallel train tracks, each at
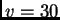 mph. You are on one train and your friend is on the other train. You
throw a heavy object directly at your friend. Neglecting air
resistance, it will land
mph. You are on one train and your friend is on the other train. You
throw a heavy object directly at your friend. Neglecting air
resistance, it will land
= 1.4in
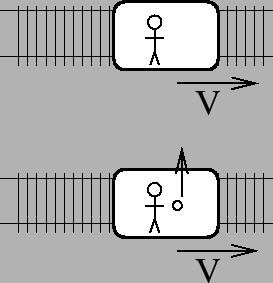
- ahead of your friend
- at (next to) your friend
- behind your friend
- need more information
- What is the average speed of a bicycle if it travels 5 m in the
first second, 6 m in the next second, and 7 m in the third second?
- A 3 kg block of ice travelling at a speed of 5 m/s on an icy
surface is a attached to a ring by a 2m long string. The string keeps
it moving in a horizontal circle. (The left side picture shows the
view form the side, the right side picture shows the view from above.)
If the string breaks suddenly,
which path will the ice block follow?
= 2in
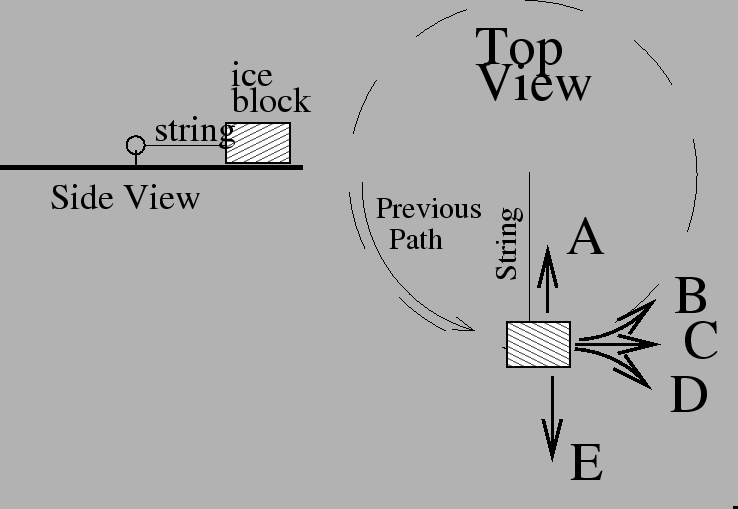
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- need more information
- A 4 kg pumpkin falls from the 2nd floor of a building and hits
the ground a time
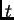 later. If you want the pumpkin to take twice as long
to hit the ground (ie:
later. If you want the pumpkin to take twice as long
to hit the ground (ie: 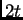 ), you should drop it from a height
), you should drop it from a height
- 1/4 as high
- 1/3 as high
- 1/2 as high
- twice as high
- four times as high
- need more information
- A 0.5 kg apple falls from a tree and hits the ground 2 sec
later. What was the speed of the apple when it hit the ground?
- I have three pieces of gold. One has a weight of 1 N on the
Moon (
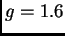 m/s
m/s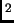 ). The second has a weight of 1 N on the
Earth (
). The second has a weight of 1 N on the
Earth (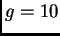 m/s
m/s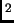 ). The third has a weight of 1 N on
Jupiter (
). The third has a weight of 1 N on
Jupiter (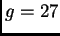 m/s
m/s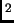 ). Which piece has the greatest mass?
). Which piece has the greatest mass?
- The one on the Moon
- The one on the Earth
- The one on Jupiter
- need more information
- The force of friction on a sliding 5 kg chair is 20 N. You push
it across the room. How much force do you have to apply once it is
moving in order to keep it moving at constant velocity?
- 0 N
- 10 N
- 20 N
- 50 N
- need more information
- I throw a 0.2 kg apple straight up at a speed of 20 m/s. Two
seconds later, what are (a) the velocity and (b) the acceleration of
the apple?
- A 1000 kg Honda Civic can go from 0 to 60 mph in 8 sec. When
the driver slams on the brakes at 60 mph, it can stop in 4
sec. Which is true?
- The brakes can apply four times as much force on the car as the engine
- The brakes can apply twice as much force on the car as the engine
- The brakes can apply equally as much force on the car as the engine
- The brakes can apply half as much force on the car as the engine
- The brakes can apply one-fourth as much force on the car as the engine
- Not enough information
- A 4000 kg truck going 30 miles per hour applies the brakes and
stops in a period of time
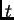 . If instead the rear brakes fail so that the
brakes only exert half as much force, how much
time would it take to stop?
. If instead the rear brakes fail so that the
brakes only exert half as much force, how much
time would it take to stop?
- one-fourth as much
- half as much
- the same
- twice as much
- four times as much
- Not enough information
- A baseball player slides into homeplate. During the slide, the
ground exerts a frictional force on the player that
decreases her speed. If this frictional force is the action force,
what is the reaction force?
- The force of gravity of the Earth on the player
- The normal force of the ground on the player
- The force of gravity of the player on the Earth
- The force of friction of the player on the ground
- Other
- Not enough information
- A 2 ton (2000 kg) Ford Explorer travelling at 20 m/s to the right and a 1/2
ton (500 kg) Mini travelling at 20 m/s to the left collide head on and stick together.
Which exerts more force on the other during the collision?
= 0.8in
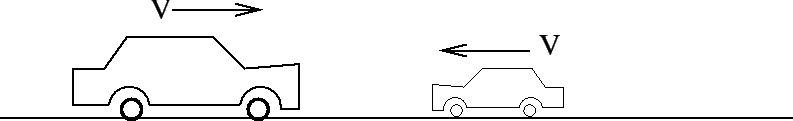
- The Explorer exerts more force on the Mini
- The Mini exerts more force on the Explorer
- Both exert the same force on each other
- Not enough information
- In the previous problem, what is the speed of the wreckage
immediately after the collision (ie:
before friction makes them slide to a halt)?
- more than 20 m/s
- 20 m/s
- less than 20 m/s but not zero
- zero
- Not enough information
- In the previous problem, in what direction is the wreckage moving
immediately after the collision (ie:
before friction makes them slide to a halt)?
- right
- left
- up
- down
- They are not moving
- Not enough information
- In the previous problem, which car has the greater change in velocity?
- The Explorer
- The Mini
- Both the same
- Not enough information
- In the previous problem, which car has the greater change in momentum?
- The Explorer
- The Mini
- Both the same
- Not enough information
- A 1 kg flowerpot falls 5 m onto the ground and shatters. What
force did the flowerpot exert on the ground?
- 1 N
- 5 N
- 10 N
- 100 N
- Other
- Not enough information



Next: About this document ...
2003-10-09


