


Next: About this document ...
to Name: Honor Code Signature:
Physics 102 Final Exam
6 May 2002
Prof L. Weinstein
There are 65 questions.
Please give a short explanation for all of your non-numerical
answers. Show your work for all numerical answers.
A table of physical data and a periodic table are at the back of the
test.
- (No explanation needed) Light will always travel from one place
to another along a path of least
- distance
- time
- effort
- expense
- complication
- The shortest plane mirror in which you can see your entire
image is (hint: draw a picture for your explanation)
- half your height
- about 1/3 your height
- about 3/4 your height
- equal to your height
- dependent on the distance between you and the mirror
- If you walk toward a mirror with a speed of 3 m/s, at what
speed are you and your image approaching each other?
- Some surfaces that are considered rough for reflecting infrared
waves may be considered polished for reflecting
- radio waves
- light waves
- both
- neither
- need more information
- (no explanation needed) Light refracts when traveling from air
into glass because light
- has a different intensity in glass than air
- has a different frequency in glass than air
- has a different velocity in glass than air
- other
- A beam of light emerges from water into air (see figure).
Which light ray comes closest to the direction of the light ray in air?
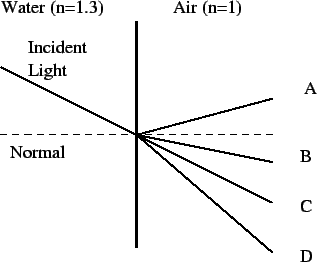
- A
- B
- C
- D
- none come close
- (no explanation needed) Rainbows are not usually seen as
complete circles because
- the ground is usually in the way
- they are actually elliptical
- they have no bottom part
- raindrops are not perfectly round
- rainbows are actually arch shaped
- If you wish to spear a fish with a regular spear, you should
compensate for refraction between the air and the water and throw your
spear (draw a picture for your explanation)
- directly at the sighted fish
- above the sighted fish
- below the sighted fish
- need more information
- When a fish looks upward at angle of 45 degrees, does it see
the sky or only a reflection of the bottom? Explain.
- A planar wave of blue light passes through a very small hole.
It then makes a bright spot on a screen a few meters away. If instead
red light passes through the hole, the bright spot will be
- larger
- the same size
- smaller
- need more information
- The colors seen when gasoline or oil forms a thin film on a
puddle of water are a demonstration of
- refraction
- reflection
- diffraction
- polarization
- interference
- What fraction of sunlight passes through a) an ideal polarizing
filter?
b) two ideal polarizing filters parallel to each other?
c) two ideal polarizing filters at right angles to each other?
- An inventor proposes to equip an office with a polarized source
of background music and let those who prefer not to hear it wear
polarizing earplugs. His idea is
- practical - it gives people a choice
- too expensive
- too much bother
- nonsense - you can't polarize a sound wave
- Camera lenses coated with a layer of transparent material of
the right thickness are almost completely non-reflective for light
near the middle of the visible spectrum. They do, however, reflect a
significant amount of
- green
- red
- white
- violet
- red and violet
- Red laser light passes through two thin parallel slits and forms
a diffraction pattern (a pattern of alternating dark and light spots)
on a screen a few meters away. The distance between adjacent light spots is
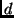 . If the two slits are moved closer together, then the spacing
between adjacent light spots will
. If the two slits are moved closer together, then the spacing
between adjacent light spots will
- increase
- decrease
- remain the same
- need more information
- You look at a thin yellow light source using diffraction glasses.
You will see
- thin lines that are the same color as the yellow light
- thin lines of different colors
- either one, it depends on the light source
- need more information
- (no explanation needed) To say that energy levels in an atoms
are discrete, is to say that the energy levels are well defined and
- separate from one another
- separated from one another by the same energy increments
- continuous
- private
- Light is emitted when an electron
- is boosted to a higher energy level
- makes a transition to a lower energy level
- swings around the atom in the same orbit
- other
- (no explanation needed) A photon of which of the colors below
has the longest wavelength?
- red
- orange
- yellow
- green
- blue
- The frequencies of light emitted by an incandescent lamp (eg: a
typical 100 W bulb) depends on the
- amount of electrical energy transformed
- temperature of the filament
- voltage applied to the lamp
- electrical resistance of the lamp
- energy differences between electron orbits in the gas inside the lightbulb
- A paint pigment that emits red light when it is illuminated
with blue light
- is fluorescent
- is phosphorescent
- is used in lasers
- is polarized
- doesn't exist
- A star has a yellow spectral line at a frequency of
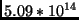 Hz. If the star is moving toward us, we will observe the
same spectral line at
Hz. If the star is moving toward us, we will observe the
same spectral line at
- a slightly higher frequency
- a slightly lower frequency
- exactly the same frequency
- need more information
- What is the energy of a red photon of frequency
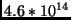 Hz? Give your answer in Joules and then convert it to electron-Volts.
Hz? Give your answer in Joules and then convert it to electron-Volts.
- What is the frequency of a blue photon of wavelength 440 nm
(nano-meters)?
- Light behaves as both a wave and a particle. Describe an
experiment or a measurement that shows that light behaves as a
particle.
- When a clean surface of potassium metal is exposed to blue
light, electrons are emitted. If the intensity of the blue light is
increased, which of the following will also increase (choose all that apply)?
- the number of electrons ejected per second
- the maximum kinetic energy of the ejected electrons
- the threshold frequency of the ejected electrons
- the time lag between the absorption of blue light and the start
of emission of the electrons
- none of these
- A proton moving at 1700 m/s has a certain wavelength. If you
double the speed, the wavelength will
- quarter
- halve
- stay the same
- double
- quadruple
- none of these
- I want to use an electron beam to study the nucleus of the atom
(diameter about
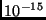 m). What electron momentum do I need?
m). What electron momentum do I need?
- Atoms can absorb energy from light or from heat. The absorbed
energy lifts the electron wave from a low orbit near the nucleus to a
higher orbit. When the atom radiates away the absorbed energy, the
electron wave drops back down to the lower and smaller orbit. In the
smallest orbit, the ground floor orbit, the electron cannot radiate
any energy because
- it has zero kinetic energy
- the wave will not fit in a lower smaller orbit
- both
- neither
- (no explanation needed) The atomic number of an element is
always the same as the number of its
- electrons
- protons
- neutrons
- nucleons
- none of these
- (no explanation needed) Different isotopes of an element have a
different number of
- electrons
- protons
- neutrons
- none of these
- The half-life of tritium, a radioactive isotope of hydrogen,
depends on (circle all that apply)
- the number of atoms in the substance
- whether it is in the form of hydrogen molecules (H
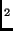 ) or
water molecules (H
) or
water molecules (H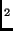 O)
O)
- the temperature of the substance
- the age of the substance
- none of these
- What are the daughter nuclei of the following decays:
a) Radioactive potassium,
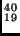 K, decays by
K, decays by 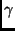 emission.
emission.
b) Sodium, 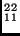 Na, decays by positive
Na, decays by positive 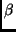 emission.
emission.
c) Americium, 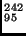 Am decays by
Am decays by 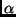 emission.
emission.
- (no explanation needed) Most of the radioactivity we personally
encounter comes from
- fallout from nuclear weapons tests
- nuclear power plants
- medical x-rays
- other man-made sources
- the natural environment
- The half-life of Carbon 14 is 5730 years. If a 1-gram
sample of old carbon is 1/8 as radioactive as 1 gram of a current
sample, how old is the sample?
- In the fissioning of Uranium, a chain reaction is caused by
- the enormous energy release
- the kinetic energy of the decay products
- ejected neutrons
- the conversion of mass to energy
- none of these
- Fissioning Helium would
- release energy
- require energy
- neither
- need more information
- Two glasses are filled with water to the same depth. One glass
has straight vertical sides and the other is V shaped (see picture).
Which glass has the higher pressure at the bottom?
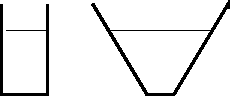
- straight sides
- V shaped
- both the same
- need more information
- At sea level, even a perfect vacuum can raise water only 10
meters up a straw. How high can you raise water up a straw in
Bozeman, Montana (elevation 5000 feet)?
- less than 10 m
- 10 m
- more than 10 m
- need more information
- Salt water is slightly denser than fresh water. Will a 1 cubic
meter, 3.5 ton rock feel a greater buoyant force at a depth of 100 m
in the
ocean or in a freshwater lake (assuming the water is the same temperature)?
- the ocean
- the lake
- both the same
- need more information
- Salt water is slightly denser than fresh water. Will a 3.5 ton
boat feel a greater buoyant force floating in the ocean or in a
freshwater lakee (assuming the water is the same temperature)?
- the ocean
- the lake
- both the same
- need more information
- A submarine in the arctic ocean (where the water is
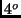 C
from surface to bottom) experiences a buoyant force of 23,000 tons
when it is at a depth of 1000 m. What is the buoyant force on the
submarine when it is at a depth of 100 m?
C
from surface to bottom) experiences a buoyant force of 23,000 tons
when it is at a depth of 1000 m. What is the buoyant force on the
submarine when it is at a depth of 100 m?
- less than 23,000 tons
- approximately 23,000 tons
- more than 23,000 tons
- need more information
- Blood flows through arteries to all parts of our body. An
aneurysm is a widening of an artery (see figure, the arrow shows the
direction of blood flow). How does the blood
pressure in the aneurysm compare to the blood pressure in the rest of
the artery?
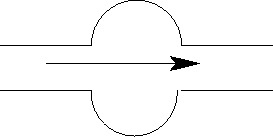
- the aneurysm blood pressure is higher
 the aneurysm
will get bigger (uh-oh!)
the aneurysm
will get bigger (uh-oh!)
- the aneurysm blood pressure is lower
 the aneurysm
will get smaller (whew!)
the aneurysm
will get smaller (whew!)
- the pressures are the same
- need more information
- A bag is filled with 2 cubic meters of an ideal gas at a pressure of 1
atmosphere and a temperature of
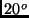 C (about 68
C (about 68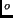 F). If the
temperature is doubled to
F). If the
temperature is doubled to 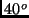 C without changing the pressure, then
the volume of the gas becomes
C without changing the pressure, then
the volume of the gas becomes
- less than 2 m
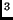
- more than 2 m
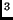 but less than 4 m
but less than 4 m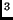
- 4 m
- more than 4 m
- need more information
- How and why would placing a large aluminum nail through a potato
before baking it affect the cooking time?
- You add 100 J of heat each to 100 g of water and to 100 g of iron.
Which material has the greatest increase in internal energy?
- the water
- the iron
- both the same
- need more information
- You add 100 J of heat each to 100 g of water and to 100 g of iron.
Which material has the greatest increase in temperature?
- the water
- the iron
- both the same
- need more information
- Which gets hotter in sunlight, a black car or a white car?
- black
- white
- both the same
- need more information
- Which gets colder on a clear night, a black car or a white car?
- black
- white
- both the same
- need more information
- A mechanic is testing an air conditioner by running it on a
workbench in an isolated room. What happens to the temperature of the room?
- it increases
- it decreases
- it stays the same
- need more information
- What input energy is required if an engine performs 200 J of
work and exhausts 400 J of heat to the cold reservoir?
- What is the efficiency of an ideal heat engine with a boiler at
200
 C that exhausts its heat at room temperature (27
C that exhausts its heat at room temperature (27 C)?
C)?
- We can treat people's legs as pendulums to analyze how they
walk. Which legs take longer to swing back and forth, those of tall
people or short people?
- tall
- short
- both the same
- need more information
- You stand just to the side of the low point of a child's swing
and always push the child in the same direction. The period of the
swing is 3 s. You push the swing at even intervals. Which intervals
will make the swing go very high (resonance)? Circle all that apply.
- pushing once every 1 s
- pushing once every 2 s
- pushing once every 3 s
- pushing once every 4 s
- pushing once every 5 s
- pushing once every 6 s
- none of the above
- If you double the speed of a wave while keeping the wavelength
fixed, what happens to the period?
- it gets 4 times smaller
- it gets 2 times smaller
- it stays the same
- it gets 2 times bigger
- it gets 4 times bigger
- need more information
- When you yell at a friend, are the air molecules that strike
his ear the same ones that left your lungs?
- Yes
- No
- (no explanation needed) When you see your friend, are the
photons that reach your eyes the same ones that bounced off her?
- Yes
- No
- Draw diagrams to show the standing wave pattern for the first
three harmonics of a rope fixed at both ends.
- A pipe organ has pipes of many different lengths. Which ones
make the highest notes?
- the shortest ones
- the middle ones
- the longest ones
- need more information
- Your real estate agent assures you that extra traffic from the
new shopping mall will only increase noise from cars by about 15%, from 60
dB to 70 dB. What does this imply about the number of cars using the
street?
- It will increase by less than 15%
- It will increase by about 15%
- It will increase by more than 15%
- need more information
- A green cloth is illuminated by magenta light. What color does
it appear?
- If you mix cyan and magenta paint, what color paint will
result? (ie: if you shine white light on the mixture, what color will
it appear?)
- Light travels through the air at
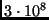 m/s and hits a
piece of glass. The light in the glass travels more slowly than the
light in the air (at about
m/s and hits a
piece of glass. The light in the glass travels more slowly than the
light in the air (at about 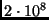 m/s). When the light
re-emerges into the air its speed is
m/s). When the light
re-emerges into the air its speed is
- less than
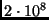 m/s
m/s
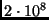 m/s
m/s
- between 2 and
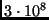 m/s
m/s
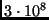 m/s
m/s
- more than
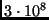 m/s
m/s
- need more information
- Why don't we see colors at night when there is a half-moon?
- Rank the following photons from least to most energetic:
radio, ultraviolet, blue, infrared, gamma ray, green



Next: About this document ...
2002-05-08

 ) or
water molecules (H
) or
water molecules (H O)
O)


 the aneurysm
will get bigger (uh-oh!)
the aneurysm
will get bigger (uh-oh!)
 the aneurysm
will get smaller (whew!)
the aneurysm
will get smaller (whew!)
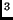 but less than 4 m
but less than 4 m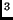
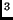
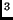
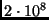 m/s
m/s
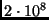 m/s
m/s
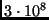 m/s
m/s
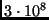 m/s
m/s
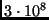 m/s
m/s