- distance
- time
- effort
- expense
- complication
This is why light bends when entering a medium with a different speed (like
the lifeguard entering the water)
- half your height
- about 1/3 your height
- about 3/4 your height
- equal to your height
- dependent on the distance between you and the mirror
We did this in class.
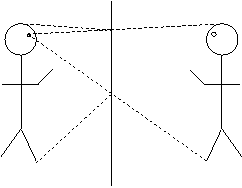
You are walking at 3 m/s and your image is moving at 3 m/s so you approach
at 6 m/s
- radio waves
- light waves
- both
- neither
- need more information
A 'rough' surface is one where the surface irregularities are bigger than
1/8 of a wavelength. Since the wavelength of radio waves (typically
meters) is MUCH larger than the wavelength of infrared waves (typically about
a millionth of a meter), you could have a surface that reflects infrared diffusely
but reflects radio waves specularly.
- has a different intensity in glass than air
- has a different frequency in glass than air
- has a different velocity in glass than air
- other
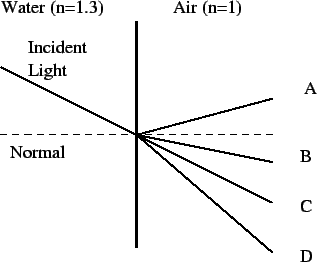
- A
- B
- C
- D
- none come close
When going from a slower medium to a faster one, light bends AWAY from the
normal.
- the ground is usually in the way
- they are actually elliptical
- they have no bottom part
- raindrops are not perfectly round
- rainbows are actually arch shaped
- directly at the sighted fish
- above the sighted fish
- below the sighted fish
- need more information
The fish appears closer to the surface than it really is.
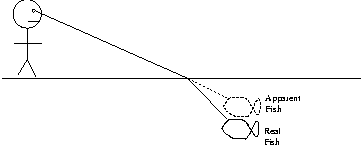
It sees the sky. The critical angle for total internal reflection in
water is 48.6 degrees. If the fish looks up at an angle greater than
this, it will only see the light from the bottom. At angles less than
this, it will see light from the sky and some light reflected from the bottom.
- larger
- the same size
- smaller
- need more information
Assuming that 'a very small hole' means that it is small compared to the
wavelength of blue light, then the size of the image is determined by the
diffraction of light. Red light has a longer wavelength so it diffracts
more so the spot will become larger.
- refraction
- reflection
- diffraction
- polarization
- interference
It is the interference between the light reflecting from the top surface
of the film (the air-gas boundary) and the light reflecting from the bottom
surface of the film (the gas-water boundary).
50%. Sun light is unpolarized so only half of it can pass through a
polarizing filter. (No explanation was needed, just the number)
b) two ideal polarizing filters parallel to each other?
50%. The light that passes through the first filter isnow perfectlyaligned to pass the second.
c) two ideal polarizing filters at right angles to each other?
None. All the light that passes through the first filter is blocked
by the second.
- practical - it gives people a choice
- too expensive
- too much bother
- nonsense - you can't polarize a sound wave
You cannot polarize a longitudinal wave, only a transverse wave.
- green
- red
- white
- violet
- red and violet
These are the colors farthest from the middle of the spectrum.
- increase
- decrease
- remain the same
- need more information
The closer the slit spacing, the wider the diffraction pattern. We
did this in class.
- thin lines that are the same color as the yellow light
- thin lines of different colors
- either one, it depends on the light source
- need more information
You can make yellow light with either a) truly yellow light or b) with a
mixture of red and green. You do not know without using diffraction
glasses which it is.
I gave half credit for answers a or b (with a suitable explanation)
- separate from one another
- separated from one another by the same energy increments
- continuous
- private
- is boosted to a higher energy level
- makes a transition to a lower energy level
- swings around the atom in the same orbit
- other
When an electron makes a transition from a higher energy level to a lower
energy level, the extra energy is radiated in the form of light.
- red
- orange
- yellow
- green
- blue
- amount of electrical energy transformed
- temperature of the filament
- voltage applied to the lamp
- electrical resistance of the lamp
- energy differences between electron orbits in the gas inside the lightbulb
Incandescent lights work by thermal radiation. The higher the temperature,
the higher the average frequency of the light emitted.
- is fluorescent
- is phosphorescent
- is used in lasers
- is polarized
- doesn't exist
This is one of the questions that I did not count toward the exam total
since we did not spend much time on this in class.
There are many pigments that glow when illuminated by black light (ie: ultraviolet).
These are fluorescent. The same principle is at work here.
- a slightly higher frequency
- a slightly lower frequency
- exactly the same frequency
- need more information
The light will be doppler shifted to a slightly higher frequency
E = hf = 6.6*10^(-34) J-s * 4.6*10^(14) 1/s = 3.0 * 10^(-19) J
3.0*10^(-19) J * [1 eV / 1.6 * 10^(-19) J ] = 1.9 eV
f = c/lambda = 3 * 10^8 m/s / 440 * 10^(-9) m = 6.8 * 10^14
1/s
I only took off one point for not remembering what nano meant.
possible answers: a) photoelectric effect (knocking out electrons with
photons)
b) discrete lines in vapor lamps
c) slow buildup of photographic images as photons arrive
- the number of electrons ejected per second
- the maximum kinetic energy of the ejected electrons
- the threshold frequency of the ejected electrons
- the time lag between the absorption of blue light and the start of emission of the electrons
- none of these
Increasing the intensity increases the number of photons but does not change
their energy. Therefore the number of electrons emitted increases but
nothing else changes.
- quarter
- halve
- stay the same
- double
- quadruple
- none of these
wavelength = h/momentum. Double velocity -> double momentum -> half
wavelength
You can't use f = c/lambda to find the wavelength since you do not know
the frequency.
You need an electron with a wavelength the size of the nucleus: lambda
= 10^(-15) m. Then
lambda = h/p -> p = h/lambda = 6.6*10^(-34) J-s / 10^(-15) m = 6.6
* 10^(-19) kg m/s
Nobody got this correct. I didn't count the question.
- it has zero kinetic energy
- the wave will not fit in a lower smaller orbit
- both
- neither
Electron orbits are fixed by the requirement that a even number of electron
wavelengths must fit around the circumference of the orbit. The lowest
orbit is where only one wavelength fits around the circumference of the orbit.
You cannot have a lower orbit than that because the electron wave won't fit.
People have proposed infinite energy schemes claiming that hydrogen has
an energy state lower than the ground floor orbit. They are lying.
Do not give them your money.
- electrons
- protons
- neutrons
- nucleons
- none of these
- electrons
- protons
- neutrons
- none of these
- the number of atoms in the substance
- whether it is in the form of hydrogen molecules (H
 ) or water molecules (H
) or water molecules (H O)
O) - the temperature of the substance
- the age of the substance
- none of these
The half life is a property of the isotope. You cannot change it.
No change. 40/19 K
b) Sodium, ![]() Na, decays by positive
Na, decays by positive ![]() emission.
emission.
22/11 Na -> 22/10 Ne + e+ + neutrino (it is emitting a positive beta particle so the number of protons must decrease by 1)
c) Americium, ![]() Am decays by
Am decays by ![]() emission.
emission.
242/95 Am -> 238/93 Np + 4/2 He (the alpha particle is a helium nucleus)
- fallout from nuclear weapons tests
- nuclear power plants
- medical x-rays
- other man-made sources
- the natural environment
If the sample has only 1/8 the activity, then 3 half-lives have elapsed.
Age = 3 * 5730 years = 17190 years
- the enormous energy release
- the kinetic energy of the decay products
- ejected neutrons
- the conversion of mass to energy
- none of these
When a neutron hits (and is absorbed by) a uranium 235 nucleus, it makes
the nucleus fission. U235 -> two large fission fragments +
neutrons. It is the neutrons that make the other uranium nuclei fission
and keep the chain reaction going.
- release energy
- require energy
- neither
- need more information
If you fission helium, you split it up into hydrogen nuclei. This requires
energy since hydrogen is less tightly bound than helium. The sun gets
its energy by fusing hydrogen into helium.
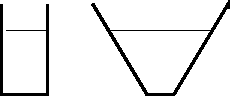
- straight sides
- V shaped
- both the same
- need more information
pressure depends only on depth and the density of the fluid.
- less than 10 m
- 10 m
- more than 10 m
- need more information
At higher altitude, air pressure is less, so it cannot raise the water as
high.
- the ocean
- the lake
- both the same
- need more information
A submerged object displaces its volume of water. The buoyant force
is the weight of the displaced water. Since salt water is denser than
fresh water, the displaced ocean water weighs more than the displaced lake
water.
- the ocean
- the lake
- both the same
- need more information
A floating object displaces its weight of water. Therefore it will
be 3.5 tons in both cases. The ship will float higher in the ocean
because it is denser, but that wasn't the question.
- less than 23,000 tons
- approximately 23,000 tons
- more than 23,000 tons
- need more information
The buoyant force doesn't depend on depth. Since the water has the
same density at 100 m and and 1000 m, the buoyancy force will be the same.
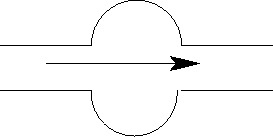
- the aneurysm blood pressure is higher
 the aneurysm will get bigger (uh-oh!)
the aneurysm will get bigger (uh-oh!) - the aneurysm blood pressure is lower
 the aneurysm will get smaller (whew!)
the aneurysm will get smaller (whew!) - the pressures are the same
- need more information
Blood flow will be slower in the aneurysm because it is wider there.
Slower flow -> more pressure (Bernoulli!).
- less than 2 m
- more than 2 m
 but less than 4 m
but less than 4 m
- 4 m
- more than 4 m
- need more information
The temperature did not really double. It only increased from 293 K to
313 K. Therefore the volume will increase, but by less than double
(PV = nRT).
Aluminum has a much higher thermal conductivity than the potato. Therefore
it will conduct heat into the middle of the potato and cook it faster.
Many restaurants do this.
- the water
- the iron
- both the same
- need more information
heat added = change in internal energy plus work done. Assuming that
neither sample does work, both will have the same increase in internal energy.
- the water
- the iron
- both the same
- need more information
Water has a much greater heat capacity than iron. Therefore, for the
same change in internal energy, its temperature will increase less.
- black
- white
- both the same
- need more information
black absorbs better
- black
- white
- both the same
- need more information
a good absorber is a good emitter. Black emits better.
- it increases
- it decreases
- it stays the same
- need more information
An air conditioner is a heat pump. It uses electrical energy to pump
heat from inside the room to outside the room. If it is sitting on
a bench in the middle of the room, then the heat will not go anywhere.
The electrical energy used by the air conditioner will turn to heat and heat
up the room.
600 J.
e = (T_hot - T_cold) / T_hot = (473 K - 300 K) / 473 K = 37%
- tall
- short
- both the same
- need more information
longer pendulums have a longer period. Tall people still walk faster
than short people (in general) because their stride is longer.
This effect is very obvious when you see people walking their dogs (especially
dachshunds).
- pushing once every 1 s
- pushing once every 2 s
- pushing once every 3 s
- pushing once every 4 s
- pushing once every 5 s
- pushing once every 6 s
- none of the above
You want to push at the same point in the swing each time. This means
waiting an even number of periods between pushes. If you push every
3 s, then you are pushing once for each swing. If you push every 6
s, then you are pushing once for every two swings.
- it gets 4 times smaller
- it gets 2 times smaller
- it stays the same
- it gets 2 times bigger
- it gets 4 times bigger
- need more information
speed = wavelength / period. Double speed -> halve period.
- Yes
- No
No. The disturbance in the air (the pressure wave) reaches his
ears. The air molecules are not shifted by the sound wave.
- Yes
- No
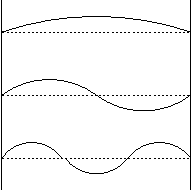
- the shortest ones
- the middle ones
- the longest ones
- need more information
The shortest ones have the shortest wavelengths and thus the highest frequencies.
- It will increase by less than 15%
- It will increase by about 15%
- It will increase by more than 15%
- need more information
An increase in noise from 60 dB to 70 dB means that the sound intensity has
increase by a factor of 10. This implies that the number of cars has
increased by A LOT!
The only color that green reflects is green. It absorbs red and blue
light. This means that it absorbs all the light that hits it so tht
it appears BLACK.
Cyan paint absorbs red light and reflects green and blue light. Magenta
paint absorbs green light and reflects red and blue light. The combinationwill
absorb both red and green, reflecting only blue.
- less than
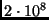 m/s
m/s -
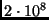 m/s
m/s - between 2 and
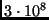 m/s
m/s -
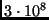 m/s
m/s - more than
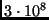 m/s
m/s - need more information
The speed is 3 * 10^8 m/s. Light slows down in materials because
it spends so much time being absorbed and reemitted by atoms. In between
atoms light always travels at 3 * 10^8 m/s.
Because there is not enough light for our cone cells to function.
radio (least), infrared, green, blue, ultraviolet, gamma ray (most)