
Most of the organic molecules you have been introduced to at this point have consisted of only carbon and hydrogen. Molecules consisting only of carbon and hydrogen are called hydrocarbons. These molecules are not very reactive and are nonpolar (do not dissolve in water). They will burn is the presence of oxygen when a high amount of activation energy is introduced. Gasoline and smaller gas molecules consists of hydrocarbons.
Biological molecules have distinctive properties which allows than to operate in their unique manner. These distinctive properties of organic molecules depends not only the hydrocarbons but also molecular components attached to the carbon skeletons. The molecular components are calle called functional groups. These functional groups will be involved in chemical and physical properties unique to the various biological macromolecules such as type of chemical reactions they may undergo and the solubility of that molecules in water. There are six functional groups that are important in the chemistry of living things. Read the pages indicated by A-7 and study behavioral objectives 23 and 24. In your notes construct a table identifying the top six functional groups, draw their structural formula and list a few properties for each group.
hydrogen -H
hydroxyl -OH
carboxyl -COOH
amino -NH2
phosphate -H2 PO4
methyl -CH3
aldehyde -CHOH
O
"
ketone- C-C-C-C
sulfhydryl -SH
Some of the properties of these functional groups are: amino group consists of nitrogen, can bind with a hydrogen bond thus making it a base,
hydroxyl group consists of a hydrogen bonded to an oxygen which in turn is bonded to a carbon skeleton, organic compounds containing hydroxyl groups are called alcohols, water is attracted to the hydroxyl groups thus making alcohols soluble in water (examples ethanol alcohol ((drinking alcohol - vodka, wine, etc.)) , methyl alcohol (wood alcohol)
aldehyde group consist of a carbon atom joined to an oxygen atom by a double bond and is located on the end of a carbon chain
carboxyl group consists of an oxygen atom double bonded to a carbon that is also bonded to a hydroxyl group (COOH), these are always fond on the end of a carbon chain and have acid properties
phosphate group consist of a phosphate anion attached to a carbon skeleton
O
|
C-O-P=O
|
O
methyl group consists of a hydrocarbon group (contains only hydrogen and carbon) and thus makes the molecule hydrophobic (nonpolar), these molecules will not mix with water.
sulfhydryl groups form covalent bonds with one another stabilizing protein chains.
In your notes draw each of these functional groups attached to a carbon skeleton.
Examine behavioral objective 24 and study the pages indicated by A-8 Write in your notes a paragraph explaining differences between an alcohol and a hydroxide.
1. Press here to check answer.
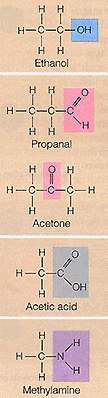
2. Identify the functional group on the carbon skeleton shown in the
top figure.
Functional groups found in biological molecules.
Press here to check answer.
3. Identify the functional group on the carbon skeleton shown in the
second figure propanal.
Functional groups found in biological molecules.

Press here to check answer.
4. Identify the functional group on the carbon skeleton shown in the
third figure acetone.
Functional groups found in biological molecules.

Press here to check your answer.
5. Identify the functional group on the carbon skeleton shown in the
fourth figure acetic acid.
Functional groups found in biological molecules.

Press here to check your answer.
6. Identify the functional group on the carbon skeleton shown in the
fifth figure methylamine.
Functional groups found in biological molecules.

Press here to check your answer.
This is the end of lesson five. During synthesis and hydrolysis
water will be split from separate molecules containing the following functional
groups:(-OH and -OH), (-NH2 and -COOH), and (-OH and
-COOH). This will be explained in the next lesson. Click here to go to
the Miniunit Alpha Lesson Page and then continue
on to lesson seven, concerning the synthesis and hydrolysis of biological
polymers.
For information on how to use this page, go to How
to Use This Site.
Created by the Center for Learning Technologies, Academic Technology Services.
Last modified October 22, 1997
.