
Picture: Trees in the Great Dismal Swamp 
The cells that make up the leaves, trunks and roots these cypress trees
are very different from the cells that make up animal cells such
as the beaver which lives nearby in its habitat (see below).

What are some of the differences between these two cell types and what
environmental conditions caused these different adaptations?
1. Click here to check your answer. click
Picture: Fern plants on a forest floor.
Do these organisms carry out the process of photosynthesis? Do they require special structures in their cells to carry out this process? The energy which drives photosynthesis comes from the sun.
What adaptive structures would these cells have to display the photosynthetic
organs in order to receive maximum sunlight?
Picture: Snakes sunning on a log.
Are these organisms able to move off of the log? What cell differences compared to plant cells would the cells of the snake have to allow this movement?
2. Click you check your answers. click
The basic structural and functional units of life are cells.
The smallest organisms consist of single cells. The largest are made
up of billions of cells, each of which maintain the characteristics of
life discussed in miniunit Alpha. Cells of all organisms are similar to
one another, both in their physical organization and their chemical processes.
A common thread found in all cell types are that individual cells are self-contained
and partially self-sufficient units bonded by an outer membrane called
the cell membrane which controls the passage of materials in and
out of the cell and all cells contain DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)
which provides a cell with a mechanism to duplicate. Review nucleic acids
by reading the pages indicated by B-1
in the text. This concept will be investigated in miniunit Gamma. DNA also
stores and provides a mechanism for the transfer of all genetic information
so that the cell can physiologically function in its own unique manner.
This allows cells to be very diverse. This concept will be investigated
in miniunit Delta. Within your own body there are more than one hundred
distinct cells types. Plants and Fungi are composed of cells that are very
different from those of your body.
.  . .
. . 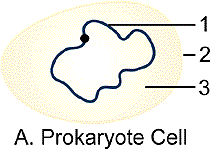
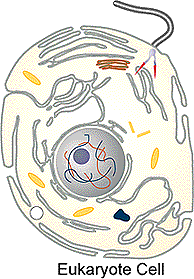
The figures above show two major types of cells - eukaryote and prokaryote. Notice the eukaryote contains many structures in its cytoplasm - red and blue linear structures represents DNA; whereas the prokaryote cell contains relative few structures in its cytoplasm - 1 = circular DNA, 2 = cell membrane, 3 = cytoplasm with ribosomes. The prokaryote cell is not only simpler than the eukaryote cell but it is also more primitive. Two prokaryote cell types you may be familiar with are unicellular bacteria and cyanobacteria (blue green algae).
By the mid 1800s several naturalists had examined cells of plants and animal and reported similarities between all cells types. From the observations three principles of the cell theory evolved.
These naturalists were Robert Hooke 1665, Anton van Leeuwenhoek 1673, Theodor Schwann 1839, Mattias Schleiden 1850 and Rudolf Virchow 1850.
The principles of the cell theory are:
A. Every living thing is composed of one or more cells.
B. The smallest living organisms are single cells, and cells are the
functional units of
multicellular organisms.
C. All cells arise form preexisting cells.
Write these in your notes.
3. Place the following molecules and structures in the correct hierarchical order going from the most simplest to the most complex. Identify these terms using the glossary in your text. Read the pages indicated by B-2 in your text.
(biosphere, cells, biomes, ecological
communities, macromolecules,
populations, tissues, organs,
organism, species, systems)
Press here to check answer. click
.
4. Which of the following cell types appeared first on Earth?
a) Eukaryote cell types in the form of unicellular amoeba.
b) Prokaryote cell types in the form of plants.
c) Eukaryote cell types in the form of multicellular animals.
d) Prokaryote cell types in the form of bacteria.
Press here to check answer. click
You must answer the following question correctly to move to
the next page.
5. Which of the following lists of cell structures are present in all cell types?
a ) cell wall, cell membrane,
DNA
b ) cell wall, cell membrane
c ) DNA cell wall, cell
membrane
d ) cell membrane only
e ) cell membrane, DNA
For information on how to use this page, go to How
to Use This Site.
Created by the Center for Learning Technologies, Academic Technology Services.
Last modified October 22, 1997.