
Living organisms consist of two fundamentally different cells types: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Readings from B-2. Prokaryotes are much more primative and structurally more simple compared to eukaryote organisms. Prokaryote cell types appeared on the Earth some 3.5 billion years ago during the precambium era. Approximately 1.4 billion years ago the first eukaryote cell type appeared on Earth. A more detailed comparison beteen these two cell types will be examined later in this miniunit. These Prokaryotes (organisms consisting of prokaryote cell types) include the bacteria (heterotrophic nutrition) and cyanobacteria (autotrophic nutrition). Heterotrophic nutrition refers to organisms that acquire their biological energy and organic carbon for growth from other organisms. You have heterotrophic nutrition. Autotrophic nutrition refers to organisms that can synthesize their own energy rich molecules from energy poor molecules. They are not dependent on other organisms for a source of biological energy and organic carbon. The most common autotrophic organisms are those that contain chlorophyll and carry out photosynthesis. You may want to go back to miniunit alpha and review the section on "characteristics of life - metabolism". Eukaryotes (organisms consisting of eukaryote cell types) include all other living forms of life which you are familiar such as: amoeba, paramecium, mosses, fungi, plants and animals. Eukaryote cells can further be classified as plant cell types, animal cell types, protista cell types and fungi cell types. You will learn the differences between plant and animal cells types in this miniunit and differences in protista and fungi cell types in a later miniunit.
Viruses are organisms that consists primarily of DNA or RNA molecules wrapped in a protein coat. These organisms can only replicate within a specific host cell by directing the machinery of that cell to synthesize viral nucleic acids and proteins. Since viruses can not grow or replicate outside of a cell and do not contain a cell membrane, they are not considered to be alive in the usual sense. Study the figure below showing a virus attacking a bacterial cell and placae in your notes.
e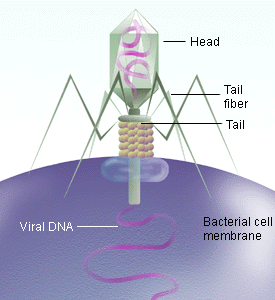
virus infecting a bacterium cell
Write in you notes the classification of the cell types discussed
above. Write a definition of autotrophic and heterotrophic nutrition.
Using the figures below identify differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic
cells.
Bacterium Cell
1 = circular DNA 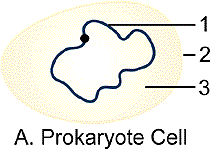
2 = cell membrane
3 = cytoplasm
Plant Cell
4 = nuclear membrane 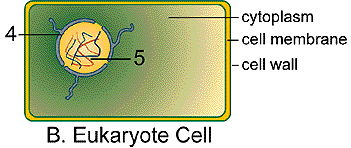
5 = DNA in the form of linear DNA
Animal Cell
lacking a cell wall 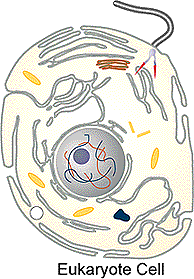
several cell organelles present in cytoplasm
In your notes write a paragraph contrasting between the four
figures above virus, bacterium, plant cell and animal cell.
6. Which of the following statements does not pertain to viruses?
a) Genome may be located on a DNA molecule.
b) Consists of a protein coat surrounding
its nucleic acid molecule.
c) Replicates inside of prokaryote or eukaryote
cells.
d) Nucleic acid molecule consists of DNA or
RNA.
e) Consists of cellular organization.
Press here to check answer. click
7. Classify the organisms listed below as:
A. prokaryotic autotroph
C. prokaryotic heterotroph
B. eukaryotic autotroph
D. eukaryotic heterotroph
1. cow 2. E. coli bacteria
3. blue-green algae 4. oak tree
1 2 3 4
a) A
C
B
D
b) C
A
B
D
c) D
C
A
B
d) D
C
B
A
Press here to check answer. click
You must answer the following question correctly to move
to the next page.
8. Which of the following "units of life" does not match the corresponding description.
a ) virus - protein coat, nucleic acids
(DNA or RNA)
b ) bacteria - prokaryote, cell membrane,
cytoplasm, circular DNA
c ) animal cell - eukaryote, organelles,
cytoplasm, autotrophic
d ) plant cell - eukaryote, organelles,
cytoplasm, photosynthesis
For information on how to use this page, go to How
to Use This Site.
Created by the Center for Learning Technologies, Academic Technology Services.
Last modified October 22, 1997.