
________________________________________________________________________
All cells Eukaryote (plant and animal), prokaryote (bacteria and blue
green algae) contain an outer cell membrane. In addition many of the structures
inside of the cell are made up of unit membrane. In this lesson you will
learn the chemical makeup and properties of membranes.
Unit membrane: 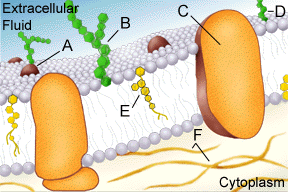
Membranes of all cells have the same basic structure. Membranes
consist of a lipid bilayer in
which are embedded globular proteins, many of which extend across
the bilayer and protrude on
either side. You may want to go back and review the molecular structure
of lipids, and phospholipids which was discussed in miniunit Alpha.
Even though the lipid bilayer provides the basic structure it has an impermeable nature; therefore, the proteins are responsible for most membrane functions. Most membranes are composed of 40 to 50 percent lipids and 60 to 50 percent protein. Not only does the cell membrane consists of unit membrane but many of the cell's organelles consist of unit membrane.
Read the pages indicated by B-4 and study behavioral objectives 2 and 3.

The figure
above represents structures found in a unit membrane. Identify the lipid
bilayer (light gray circular structures with two tails hanging in
the center), various proteins (these may extend through the lipid bilayer
or float on either surface), carbohydrate polymers (these may be attached
to lipid molecules - glycolipids or to protein molecules - glycoprotein),
cholesterol molecules (indicated by the letter E), cytoskeleton (indicated
by F the cytoskeleton are actually protein attachments which extend into
the cytoplasm).
In your notes draw a figure showing the structure of unit membrane including
the following structures: phospholipid bilayer (include the hydrophobic
tails and hydrophilic heads), proteins (include both extrinsic and intrinsic),
carbohydrates (glycolipid and glycoprotein), cholesterol, pores. The
phospholipid layer makes the membrane impervious to water and polar molecules.
In your notes explain hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic tails in relation
to polar and nonpolar properties. You may want to go back and review nonpolar
compounds (lipids) and polar compounds (water) in miniunit alpha.
In your notes fill in the table below indicating four functions of
the cell membrane.
Membrane Function Write how function is accomplished
| isolation from environment | |
| transport regulation | |
| communication | |
| identification |
Click ere to go back to readings in membrane bound organelles. click
For information on how to use this page, go to How to Use This Site.Created by the Center for Learning Technologies, Academic Technology Services.
Last modified October 22, 1997.