
Study behavioral objectives 25, 27, 29 and 31. Read the pages in the text indicated by A-10 concerning protein. Proteins are macromolecules which contain the elements carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and may contain sulfur. Proteins are polymers of amino acids. Proteins are extremely important in cell structure and function. Among the cellular functions of proteins are structural support, protection, catalysis transport, defense, regulation, and movement. Of particular importance are the catalytic proteins called enzymes.
Proteins are polymers of amino acids. There are approximately twenty different types of amino acids. Proteins can vary in length from two amino acids to a chain of millions of amino acids (polypeptide).
Two amino acids synthesized together = dipeptide
Three amino acids synthesized together = tripeptide
Four to billions amino acids synthesized together = polypeptides or protein
Examples of protein are hair, claws, egg albumin, gelatin, etc.
In order to understand proteins let us examine the general structure of amino acids.
three amino acids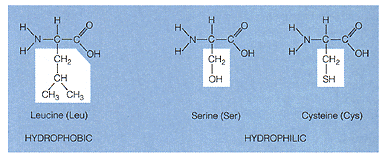
Amino Acid Structure: Amino acids consist of a
carbon skeleton consisting of one carbon with three attached groups.
Carboxyl group - this in the functional group studies earlier. -(-COOH)
The carboxyl group will be on one end of the amino acid molecules
and will provide the -OH group to form water during condensation
synthesis of amino acids to form protein. Amino group - this
is the functional group studied earlier. (-NH ) The amino group will be
on the opposite end of the amino acid as the carboxyl group and will
provide the -H group to form water during the condensation of
synthesis of amino acids to form protein. "R" group - this group may
be any of the twenty different groups of atoms which provide the protein
with its characteristics. Your text will show a few of these twenty different
types. These groups vary is structure, thus there are twenty
different types of amino acids.
amino acids
The above figure contains the structural formula for three amino acids.
Fine the amino group, carboxyl group and the "R" group. The "R" group is
outlined in white. In nature their are approximately twenty different
types of amino acids based on the "R" groups. These "R" groups produce
the chemical properties of the amino acids and the proteins which they
makeup.
17. In your notes draw a figure showing the general
structural formula of an amino acid.
Amino acids are hooked together to forming covalent bonds between the
amino acid monomers. This is accomplished as discussed earlier by
condensation synthesis. Let us review condensation synthesis: During
the process of condensation synthesis one water molecule between each monomer
will be removed. Each monomer contributes part of the water molecule
that is released; one monomer loses a hydroxyl group (OH), and the other
loses a hydrogen (H). Both monomers, having each lost a covalent
partner, now bond covalently with each other. This time the OH is
removed from the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the H is removed
from the amino group of a second acid amino acid. Trace the events
described above using the figure below.
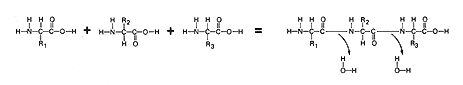
18. How many water molecules will be formed when four amino acids
condense to form a protein molecules?
In your notes using structural formulas write a reaction hooking three
amino acids together during a synthesis condensation reaction.
Note that the bond which forms during the synthesis of two or more
amino acids contains a C-N-C bond since water is cleaved between an amino
group and an organic acid group. This bond is called a peptide bond.
It exists only in proteins. Locate th two peptide bonds in the protein
molecule below.

19. How many peptide bonds does a tripeptide contain?
Not only do different protein contain different lengths of amino
acids, but the amino acids can be arranged in any order. Therefore their
is almost an infinite number of proteins.
The precise sequence of amino acids in a protein is called its primary
structure.
20. What is the primary structure of the following protein?
ser-gly-gly-glut-arg-thre
21. Protein can also be hydrolyzed. If you had eggs for breakfast this
morning the protein of the egg albumin (egg white) is in your large intestine.
This protein is now being hydrolyzed (digested) into what products?
Click here to go back to lesson. click
Created by the Center for Learning Technologies, Academic Technology Services.
Last modified October 22, 1997.