Study behavioral objectives 41-42
and read the pages indicated in the text by E-23.
During the section on cellular respiration you studied the mitochondrion
which produces ATP by breaking down energy rich molecules (glucose). ATP
is the only source of energy which can be used by biological systems.
 Another
organelle that makes ATP energy molecules is the chloroplast.
Another
organelle that makes ATP energy molecules is the chloroplast.
Chloroplasts use energy from sunlight to make ATP which in turn is used to build energy rich molecules (glucose), whereas mitochondria make ATP using energy from energy rich molecules.
Plant cells often contain a variety of membranous plastids, with
names such as those below. Click on the common green plastid that uses
light energy to make ATP molecules.
| chloroplast | leucoplast |
| chromoplast | proplastid |
Using light and energy rich molecules , respectively, chloroplasts and mitochondria make molecules that supply energy for growth, motion, response to stimuli, etc. What are these energy molecules called? (ATP/DNA/RNA)
 Both
organelles produce the ATP molecules that supply energy for most cell processes.
Both
organelles produce the ATP molecules that supply energy for most cell processes.
- a. Which organelle uses light to make ATP?
- b. Which uses energy rich molecules and oxygen to make ATP?
- c. Which organelle is not found in animal cells and non-green plant cells?
- d. Which is found in both plant and animal cells?
- e. Which organelle is often called the "powerhouse of the cell"?
(mitochondrion/chloroplast)
(mitochondrion/chloroplast)
(mitochondrion/chloroplast)
(mitochondrion/chloroplast)
(mitochondrion/chloroplast)
Although the mitochondrion is called the "powerhouse of the cell," the energy to make the energy rich molecules used by mitochondria comes from light energy harnessed by chloroplasts.
 Chlorophyll,
the green-colored chemical that actually absorbs light energy, is located
within the chloroplast in the stacks of membranes called grana.
In higher plants there are two chlorophyl molecules, chlorophyl l
"a" and chlorophyl l "b". Both of these molecules can absorb red and blue
light which in turn is used for photosynthesis. In the earlier web page
you learned that only chlorophyll "a" was used in the photosystems to convert
light energy into chemical energy. Chlorophyll "b" can also absorb light
energy and pass it on to the chlorophyll "a" pigment by a process called
electron resonance. Also recall that you studied how a proton pump works
across membranes in the chloroplast. This occurs in the grana. Look
at the grana in the chloroplast.
Chlorophyll,
the green-colored chemical that actually absorbs light energy, is located
within the chloroplast in the stacks of membranes called grana.
In higher plants there are two chlorophyl molecules, chlorophyl l
"a" and chlorophyl l "b". Both of these molecules can absorb red and blue
light which in turn is used for photosynthesis. In the earlier web page
you learned that only chlorophyll "a" was used in the photosystems to convert
light energy into chemical energy. Chlorophyll "b" can also absorb light
energy and pass it on to the chlorophyll "a" pigment by a process called
electron resonance. Also recall that you studied how a proton pump works
across membranes in the chloroplast. This occurs in the grana. Look
at the grana in the chloroplast.
 The
two major energy organelles have similar structures.
The
two major energy organelles have similar structures.
The inner membrane of the mitochondrion is folded in shelves called cristae, while the inner membrane of the chloroplasts forms stacks called grana.
Each granum of a chloroplast consists of a stack of thylakoids (special cisternae). Thylakoids are flattened membranous sacs studded with chlorophyll-containing particles called quantasomes. Look at the thylakoids and quantasomes below.
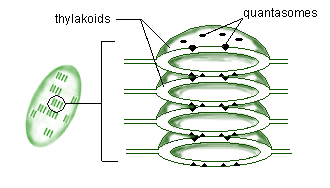
Quanta are units of light energy, so chlorophyll-containing bodies
(-somes) within chloroplasts that use light quanta to make ATP are
called quantasomes.
From the previous lesson you have learned that there are two sets of reactions which occur during photosynthesis - light reactions and dark reactions. Also you learned that ATP and NADPH produced during the light reactions (light dependent) are used to reduce carbon during the dark reactions (light independent). Therefore, there must be a close connection between these two pathways. Both sets of reactions occur in the chloroplast. The dark reactions occur in the stroma of the chloroplast and the light reactions occur in both stroma and grana thylakoids.
 You have now
completed the readings for Miniunit Epsilon.
You have now
completed the readings for Miniunit Epsilon.
Created by the Multimedia Development Lab, Academic Technology Services.
Last modified October 29, 1997.