Study behavioral objectives 25-26 and read the pages indicated by E-15.
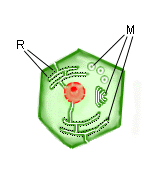 Except
for ribosomes (R), the organelles (M) are all continuous
or capable of fusing with the plasma membrane of a cell. To review, name
the missing one of these three membranous organelles.
Except
for ribosomes (R), the organelles (M) are all continuous
or capable of fusing with the plasma membrane of a cell. To review, name
the missing one of these three membranous organelles.