
Read the pages indicated by G-10 and study behavioral objectives 22 and 23 . Meiosis is similar to mitotic cell division studied earlier. The difference between meiosis and mitosis is that there are two sets of nuclear divisions during the meiotic cell cycle. The first process (meiosis I) includes a reduction of chromosomes. The second process (meiosis II) is a normal mitotic division as studied earlier; however, no DNA replication occurs prior to prophase II. The overall effect of meiosis is the reduction in chromosome numbers of a diploid cell by one-half.
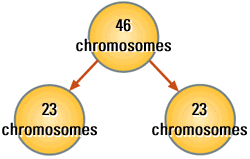
Examine the figure below. Even more important this reduction of chromosomes
is not random, but is separates the homologous chromosome pairs of a diploid
cell into four cells which contain only one of each homologous pair
(haploid cells). This concept is very important. In your notes draw
figures representing diploid and haploid cells.
1. Click here for the definition of diploid cells and haploid cells.
click
A cell preparing to undergo meiosis will pass through the
S and G2 stage similar to the mitotic cell cycle during the interphase
stage. Remember that during the S stage DNA replication occurs. The
cell than moves into the first meiotic phases which are divided into four
stages similar to that of mitosis - prophase I (chromatin forms into chromosomes)
, metaphase I (chromosomes line up along an equatorial plate), anaphase
I (chromosomes are pulled to opposite poles) and telophase I (chromosomes
reform back into chromatin forming a nucleus and cytokinesis occurs
forming two cells with each cell containing one of each homologous
pair of chromosomes). This process is called reduction
division. The second meiotic process is also divided into four stages
- prophase II , metaphase II, anaphase II and telophase II. Since both
cells which are formed during meiosis I undergoes this process the end
result will be a total of four cells with each cell containing one of
each homologous pair of chromosomes. This process is a normal mitotic division
with no DNA replication prior to prophase II.
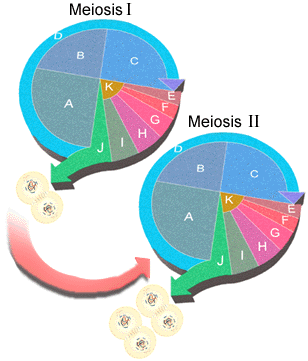
Examine the figures below. Draw these cell cycles in your notes
showing a single diploid mother cell being transformed into four haploid
daughter cells. Note: There is no synthesis stage "B" during the second
meiotic cell cycle.
 Read in your text the description
for the eight phases of meiosis (G-10). Write in
your notes a description of what occurs to the following structures
during each of these phases: chromatin, chromosomes,
centrioles, nucleoli, nuclear membrane, spindle apparatus (spindle
fibers), centromeres, tetrads. These phases are discussed in the next lesson.
Read in your text the description
for the eight phases of meiosis (G-10). Write in
your notes a description of what occurs to the following structures
during each of these phases: chromatin, chromosomes,
centrioles, nucleoli, nuclear membrane, spindle apparatus (spindle
fibers), centromeres, tetrads. These phases are discussed in the next lesson.
In your notes draw a cell containing six homologous pair of chromosomes during interphase as it appeared when you were studying mitosis.
2. Click here to compare your figure to the correct answer.
click
3. The cell in the above figure represents a diploid or haploid cell?
Press here to check answer. press
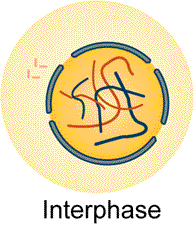
4. The cell represented in the figures above is in which stage of the
cell cycle?
a) G1
b) G2
Press here to check answer. press
5. Draw this cell with its chromosome compliment as it would
appear during the G2 stage.
Press here to check answer. press
Click here to study the phases of meiosis. click
For information on how to use this page, go to How
to Use This Site.
Created by the Center for Learning Technologies, Academic Technology Services.
Last modified October 22, 1997.