
Draw in your notes a figure showing a cell containing three pair of chromosomes as it would appear during prophase of mitosis. See figure below:
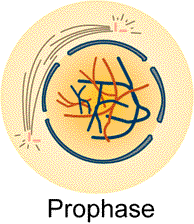
Meiosis: Prophase I
Study the figures in text indicated by G-11. From the readings write a description of the events which occur during prophase I of meiosis.
Compare your description of these events with the ones listed
below.
Prophase I -
1. Nuclear membrane pulls
apart and becomes part of the E.R. and the
nucleoli dissolves (disappears).
2. Each DNA molecule twists
and coils back on itself to form rod shaped
chromosomes.
3. Centrioles separate and
a new centriole develops at the base of each
parent centriole forming two centriole organizing centers.
These centriole
organizing centers than migrate to poles on opposite sides
of the nucleus.
4. Spindle apparatus fill
form from microtubules. Spindles will form between
centromeres of each chromosome and each centrilole
organizing center,
spindles will form between both centriole organizing centers, spindles
will
radiate out behind the centrioles and form asters.
5. The chromosomes at this
time are attracted to one another in the following
manner. Homologous chromosome pairs are attracted to one another.
This process
is calle synapsis and the resulting groups of four chromatids
are called tetrads. Locate the three sets of tetrads
in the figure below.
Draw and label this figure in your notes.

Meiosis: Prophase I, Tetrads

Examine the diagram above showing three pairs of chromosomes
as they would appear during prophase I. Each chromosome consists
of two chromatids (example - two long red or two long blue) held
together by a centromere. The two chromatids bound together
by a centromere are called sister chromatids. The original parent chromatid
was the DNA molecule of the parent cell and the attached
chromatid was formed during the S stage of interphase. Homologous chromosomes
(example one long red set and one long blue set) are attracted
to one another so that there are four chromatids lined up (tetrads).
6. How many chromosomes are represented in the figure above?
a) 0 b) 3 c) 6 d) 12
Press here to check answer. press
Study the figure below and answer the following question.

7. How many chromatids are represented in this figure?
a) 0
b) 3 c) 6 d) 12
Press here to check answer. press
Study the figure below and answer the following question.

8. How many tetrads are represented in this figure?
a) 0 b) 3 c) 6 d) 12
Press here to check answer. press
Study the two figures below and compare prophase of mitosis with
prophase I of meiosis. Write the difference in your notes.
 compare these two
figures
compare these two
figures
Meiosis: Tetrads with Genes
Note the three sets of tetrads in the figure below. The next step to
to place genes (using letters -upper case for dominant and lower case for
recessive) on the chromosomes and observe how the genes segregate
during meiosis.

In the figure below genes have been placed on the long (G,T, and
R), medium (A) and short (B) chromosomes. The "O's" represent kinetochores.
Set "A" is one of each homologous pair and set "B" is the other set.
The figure depicts three sets of homologous pair as they would appear
during prophase I (except the tetrads would scattered and not in a linear
arrangement. The four long structures represent one tetrad , four medium
structures represent a second tetrad and the four short structures
represent the third tetrad . Draw these tetrads with corresponding genes
in your notes. ,
k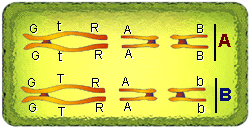
In somatic cells chromosomes usually exist in pairs. One of the pair
came from the mother (ex. Set A) and the other from the father (ex. Set
B). Homologous pair refers to those pair of chromosomes
that have the same gene sequence; however the genes do not have to
be identical. For example in this figure the genes are represented
by the letters G, T, and R. If the gene for length of stems
in plants (tall or short) is represented by the
letter "T" , the upper case (T) represents tall and lower case (t)
represents short. (same for G and R) in this figure. The chromosomes
with the genes G, T, and R in set "A" and "B" are homologous because they
have the same gene sequence. Note that in one set the "T" is upper
case and in the homologue the "T" is lower case.
Study the figure below and answer the following question.
_
k
9. How many homologous pair of chromosomes are in the figure above?
a) 1
b) 3 c) 6
d) 12
Press here to check answer. press
Study the figure below and answer the following question.
k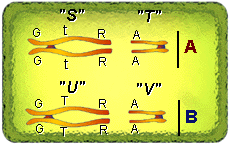
10. Which chromosomes are homologous?
a) U and V : S and T
c) S and U : T and V
b) T and S : V and U
d) none of these
Press here to check answer. press
Study the figure below and answer the following question.
k
11. Identify the tetrads.
a) S and U : T and V
c) S, U, T, and V
b) T and S : V and U
d) none of these
Press here to check answer. press
Meiosis: Metaphase I
Metaphase I - This is an easy stage to identify.
The chromosomes (tetrads) are aligned along the equator of
the cell. This accomplished by the spindles that are attached to
its kinetochore. Study behavioral objective 22 and the figures included
in the readings indicated by G-11.
Study the figure below and answer the following question.
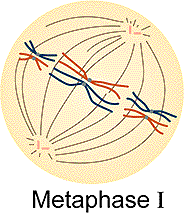
12. How many kinetochores are present on each centromere?
a) 0 b)2 c) 6 d) 12
Press here to check answer. press
Study the figure below and answer the following question.

13. Describe the arrangement of the alignment of
chromosomes along the "equator" in relation to the centrioles.
a. The equator runs parallel
to a line running between the two centriole
organizing
poles.
b. The equator runs perpendicular to
a line running between the two centriole
organizing poles.
c. The equator connects the two centriole
organizing poles.
Press here to check answer. press
In the figure below genes have been placed on the long
(G,T, and R), medium (A) and short (B) chromosomes. The "O's" represent
kinetochores. Set "A" is one of each homologous pair and set "B"
is the other set. The figure depicts three sets of homologous
pair as they would appear during metaphase I. Note that they are lined
up along the equator with homologous chromosomes paired on top of one another.
The four long structures represent one tetrad , four medium structures
represent a second tetrad and the four short structures represent
the third tetrad . Draw these tetrads with corresponding genes in your
notes.
k
Meiosis: Anaphase I
Anaphase I - Homologous chromosomes
are pulled to opposite poles of the cell. The chromosomes
consist of two sister chromatids which remain attached at the centromere
(compare this to mitosis). One of each homologous pair
with attached chromatids are pulled by the spindles which
are attached to the kinetochore located on the centromere. Study behavioral
objective 22 and the figures included in the readings indicated by G-11.
Study the figure below and answer the following question.
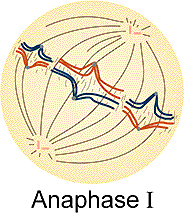
14. How many chromosomes of each homologous pair
are being pulled to each centriole organizing pole?
a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 6
Press here to check answer. press
In the figure below genes have been placed on the long (G,T, and R), medium (A) and short (B) chromosomes. The "O's" represent kinetochores. Set "A" is one of each homologous pair and set "B" is the other set. The figure depicts three sets of homologous pair as they would appear during anaphase I. Note that homologous chromosome pairs are being pulled apart (indicated by the vertical lines). The four long structures represent one tetrad , four medium structures represent a second tetrad and the four short structures represent the third tetrad . Draw these tetrads with corresponding genes in your notes.
k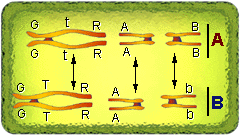
Meiosis: Telophase I
Telophase I - When the chromosomes reach the poles
the following events occur:
1. Nuclear membrane and nucleoli reform.
2. Chromosomes uncoil and untwist to reform
chromatin.
3. Spindles break down and disappear.
4. Centrioles remain next to the nucleus.
Study behavioral objective 22 and the figures included in the
readings indicated by G-11.
Study the figure below and answer the following question.
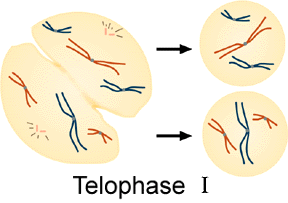
15. How many chromosomes are present in each of these cells?
a) 3 b) 6 c) 12 d) 24
Press here to check answer. press
16. The chromosomes at this stage consist of two sister
chromatids held together by a centromere.
a) true b) false
Press here to check answer. press
Study the figure below. At the end of telophase I there are two cells.
Each cell contains only one of each homologous pair (one long, one medium,
and one short). The chromosomes are still in their duplicated form (two
chromatids per chromosome). At this point the two nuclei are haploid.

In the figure below genes have been placed on the long
(G,T, and R), medium (A) and short (B) chromosomes. The "O's" represent
kinetochores. Set "A" is one of each homologous pair and set "B"
is the other set. The figure depicts three sets
of homologous pair as they would appear during telophase I. Note
that homologous chromosome pairs are separated into two cells indicated
by the double line. Draw these tetrads with corresponding genes in your
notes.
k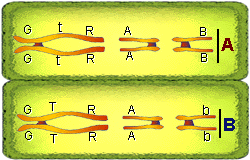
Note that the chromosomes (3) in each cell (separated by double
line) are haploid (one of each pair present) and are not genetically
alike.
Meiosis: Prophase II
Meiosis II is a normal mitotic division. The stages will be exactly like the mitotic stages studied earlier, except the two mother cells (prophase I) will be haploid and the end result will be four haploid daughter cells.
Examine the figure below. The two cells at the right would correspond
to the cells at prophase II. During the second meiotic division,
there will be no DNA replication prior to prophase II.

"A" "B"
The two cells above
the letter "B" represent the two mother cells during prophase I.
1. Nuclear membrane
pulls apart and becomes part of the E.R. and the
nucleoli dissolves (disappears).
2. Each DNA molecule
twists and coils back on itself to form rod shaped
chromosomes.
3. Centrioles separate and
a new centriole develops at the base of each
parent centriole forming two centriole organizing centers. These
centriole
organizing centers than migrate to poles on opposite sides of the
nucleus.
4. Spindle apparatus fill
form from microtubules. Spindles will form between
centromeres of each chromosome and each centrilole organizing
center,
spindles will form between both centriole organizing centers, spindles
will
radiate out behind the centrioles and form asters.
Study behavioral objective 22 and the figures included in the
readings indicated by G-11.
Examine the diagram below showing three pairs of chromosomes as they would appear during prophase II. Each chromosome consists of two chromatids held together by a centromere. The two chromatids bound together by a centromere are called sister chromatids. At this point there is only one of each homologous pair present; therefore the nuclei are haploid.
Study the figure below and answer the following question.

17. How many chromosomes per cell are represented in this figure?
a) 0 b) 3
c) 6 d) 12
Press here to check answer. press

18. How many chromatids per cell are represented in
this figure?
a) 0 b) 3
c) 6 d) 12
Press here to check answer. press
19. How many centromeres per cell are represented in this
figure?
a) 0 b) 3
c) 6 d) 12
Press here to check answer. press

The figures above may also represent prophase II.
During prophase II of meiosis the homologous chromosomes are
not in pairs. See the figure above.
There are only three chromosomes per cell.
In the figure below genes are added to the chromosomes. In this figure the genes are represented by the letters G, T, and R. If the gene for length of stems in plants (tall or short) is represented by the letter "T" , the upper case (T) represents tall and lower case (t) represents short. (same for G and R) in this figure. Note that set "A" chromosomes is in one cell and set "B" is in a different cell (separated by the double line). Each cell has a haploid number of chromosomes (the chromosomes are not in pairs).
k
20. How many homologous pair of chromosomes per cell are in this figure?
a) 0 b) 2 c) 3
d) 6
Press here to check answer. press
k
21. How many chromosomes are present in each cell?
a) 0 b) 2 c) 3 d) 6
Press here to check answer. press
This is an easy stage to identify. The chromosomes are aligned along the equator of the cell. This accomplished by the spindles that are attached to its kinetochore. Using the figures in the text compare metaphase of mitosis, metaphase I of meiosis, and metaphase II of meiosis. There are no homologous chromosomes located in the metaphase II stage. Draw these three stages in your notes. Include three sets of chromosomes. In the figure below genes have been added to the chromosomes. At this stage their are two cells ("A and B"). Each cell contains three chromosomes (L, M and N). These chromosomes are not paired.
k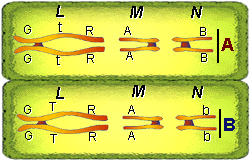
22. How many chromatids per chromosome in cell "A" or cell "B"?
a) 0 b) 2 c)
3 d) 4
Press here to check answer. press
k
23. Are the chromosomes in cell "A" genetically like the chromosomes
in cell "B"?
Press here to check answer. press
In each cell (cells "A" and "B") sister chromatids are pulled to opposite poles of the cell. Each cell has three chromosomes (L,M, and N). Up to this time each chromosome consists of two sister chromatids. The centromeres "O" split and the chromatids are pulled by the spindles which are attached to the kinetochore located on the centromere. This is represented by the vertical line Note that the chromosomes are not in pairs like they were during mitosis.
k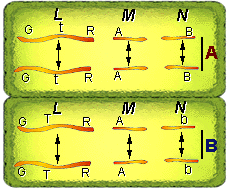
24. How many chromatids are being pulled to each
centriole organizing pole?
a) 2 b) 3
c) 6 d)
12
Press here to check answer. press
This stage is the opposite of prophase. When the chromosomes reach the poles the following events occur:
1. Nuclear membrane and nucleoli reform.
2. Chromosomes uncoil and untwist to reform
chromatin.
3. Spindles break down and disappear.
4. Centrioles remain next to the nucleus.
The cells under "A" represent prophase II chromosomes and the cells
under "B" represent telophase II chromosomes. Study the figure below and
answer the following questions.
A
B
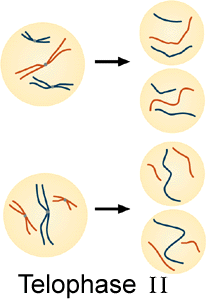
"A"
"B"
25. How many chromosomes are present in each of these cells (B)?
a) 2 b) 3 c) 6 d) 12
Press here to check answer. press

"A"
"B"
26. The chromosomes at this stage (B) consist of two sister
chromatids held together by a centromere.
a) true
b) false
Press here to check answer. press
The figure below represents the four cells formed by meiosis along
with their genetic make-up. Each cell contains three chromosomes (L,M and
N). These chromosomes are not in pairs; therefore the nuclei are haploid.
k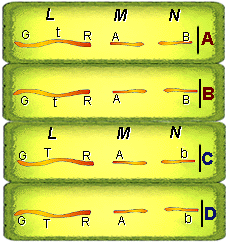
Note that two of the cells contain a "B" and two "b".

Study behavioral objective 23, 24 and 25. In your notes write
out a definition contrasting between diploid and haploid cells; somatic
and sex cells. Diploid cells contain homologous pairs of chromosomes.
One of each homologous chromosome pair was furnished by the mother
and the other by the father. Haploid cells contain one
half the number of chromosomes as a diploid since they contain only
one of each homologous chromosome pair. Haploid cells
are formed as the end result of meiosis. Only diploid
cells can under go meiosis however both diploid and haploid
cells can undergo mitosis. In higher plants and animals meiosis occurs
in special organs (sex organs). The haploid cells that are the end result
of meiosis will develop into sex cells (gametes). Male gametes are
called sperm and female gametes are called eggs or ovum. In
contrast to sex cells the cells that make up the rest of an organism
are called somatic cells. Usually in higher plants and animals somatic
cells are diploid.
27. How many chromosomes are in your somatic cells?
a) 12 b) 23
c) 24 d) 46 e)
48
Press here to check answer. press
28. How many chromosomes in your somatic cells did you receive from
your mother?
a) 12 b) 23 c) 24 d) 46 e) 48
Press here to check answer. press
29. How many chromosome pair are the in the human
sperm cell?
a) 0 b) 23 c) 30 d) 46
Press here to check answer. press
30. Which cells contain homologous pairs of chromosomes?
a) egg
b) sperm c) gametes
d) human bone cell
Press here to check answer. press
Meiosis provides a means for chromosomes to segregate out individually
from one another. Genes located on separate chromosomes will
also segregate out independently from one another. However,
genes located on the same chromosome can not segregate independently
from one another. For example during Prophase I above the genes
" G,t, and R" were located on the same chromosome and "G,T and R"
on its homologue. How do these genes (genes located on the same chromosome)
segregate out from one another, or will the gene G always be linked to
t and r ? Linked genes may be switched with its homologue by a process
called crossing over. This process occurs during Prophase I of
meiosis. The next web page will explain crossing over and show that
linked genes on one chromosome may be switched with the genes on
its homologue. Click here to go to
the next web page.
.
For information on how to use this page, go to How
to Use This Site.
Created by the Center for Learning Technologies, Academic Technology Services.
Last modified October 22, 1997.