
Read the pages indicated by G-12
and study behavioral
objective 26. Crossing over is a process where homologous pair
of chromosomes can swap pieces of DNA (genes) with one another before meiosis
is completed. This allows for gene variability of linked genes that can
be passed on to the offspring. Genes on the same chromosome would be permanently
linked if it were not for crossing over. This phenomena occurs only
during prophase I of meiosis during synapsis and tetrad formation. You
may want to go back to the previous lesson and review synapsis and tetrads.
Click here to review synapsis. click
Figure represent synapsis of one homologous pair.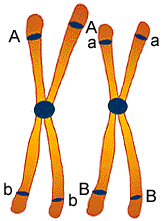
Study the figure above. "A" genes are linked to "b" genes
and "a" are linked to "B" genes. Since these genes are linked during
the transfer of hereditary material the phenotype corresponding to "A"
will always be associated with the phenotype corresponding with "b".
Example: In humans the gene which controls facial freckles is linked to
the gene for red hair. Therefore most individuals with red hair have
facial freckles. Crossing over allows a means for the gene expressing
the red hair phenotype to be on the same chromosome as the gene which does
not produce facial freckles.
1. During which phase of the cell cycle does crossing over occur?
a) prophase of mitosis
d) prophase II of meiosis
b) anaphase I of meiosis
e) both a and c
c) prophase I of meiosis
Press here to check answer. press
2. In the figure below, which genes would be linked together
in the male or female gametes if their was no crossing over?
a) "A" and "b"
d) "a" and "b"
b) "A" and "B"
e) both answer a and c
c) "a" and "B"

Press here to check answer. press
Read in the text the section G-12
concerning crossing over and study the figure below. This figure shows
the consequence of crossing over of the homologous chromosome pair above.
Write in your notes a description of crossing and identify a chiasma
which is indicated by "*" on the figure below.

Examine the figure below and and answer the following question.

3. In the figure above which genes would be linked after crossing over.
a) "A" and "b"
d) "a" and "b"
b) "A" and "B"
e) both answer b and d
c) "a" and "B"
Press here to check answer. press
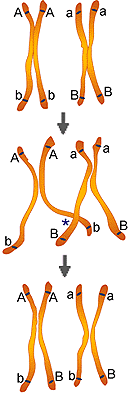
Note that only the inside chromatids crossed over; therefore, the outside
chromatids could form haploid cells with no crossovers. The four
types of haploid cells that may occur during meiosis are: (A linked
to b, a linked to B) non crossovers and (A linked to B, and a linked to
b) crossovers. In you notes draw these figures to show how these four chromosomes
are formed. Identify the chiasma of the figure in your notes.
Read pages indicated by G-13 Draw in your notes a figure comparing the prophase, metaphase, and anaphase stages of mitosis and meiosis. Study behavioral objective 24 and answer the following questions.
4. Which of the following statements is true
when comparing the anaphase stage of mitosis, meiosis I, and meiosis
II?
a) During mitosis and meiosis I sister chromatids split and are pulled to opposite poles; whereas, during meiosis II homologous chromosomes are pulled to opposite poles.
b) During mitosis and meiosis II sister chromatids split and are pulled to opposite poles; whereas, during meiosis I homologous chromosomes are pulled to opposite poles.
c) During meiosis II sister chromatids split and are pulled to opposite poles; whereas, during mitosis and meiosis I homologous chromosomes are pulled to opposite poles.
d) During mitosis sister chromatids split and are pulled to opposite poles; whereas, during meiosis I and meiosis II homologous chromosomes are pulled to opposite poles.
e) During meiosis I and meiosis II sister chromatids split and
are pulled to opposite poles; whereas, during mitosis homologous
chromosomes are pulled to opposite poles.
4. Press here to check answer. press
5. Can a cell with a diploid complement of 24 chromosomes undergo mitosis? If the answer is yes how many chromosomes will be in the daughter cells?
Press here to check answer. press
6. Can a cell with a haploid complement of 12 chromosomes undergo mitosis? If the answer is yes how many chromosomes will be in the daughter cells?
Press here to check answer. press
7. Can a cell with a diploid complement of 24 chromosomes undergo meiosis? If the answer is yes how many chromosomes will be in the daughter cells?
Press here to check answer. press
8. Can a cell with a haploid complement of 12 chromosomes undergo
meiosis? If the answer is yes how many chromosomes will be
in the daughter cells?
Press here to check answer. press
Questions 9 and 10. A diploid somatic cell contains a total
of six chromosomes.
9. How many homologous pair of chromosomes are present in this
cell ?
a) 0 b). 3 c) 6 d). 12
Press here to check answer. press
10. How many "different" sets of chromosomes in each cell may be produced when this cell (diploid somatic cell with six chromosomes or three pair) undergoes meiosis? (Hint: Draw three pair of chromosomes with different genes. The homologous pair should have the same letter with one containing an upper case and the other a lower case. (ex. Aa, Bb, and Cc). How many ways can you arrange these into haploid cells so that each cell contains one of each letter? (ex. ABC,ABc,etc.).
a) 2
b) 4 c) 8 d) 16
Press here to check answer. press
11. Review question:
If the dominate alleles R and S are linked on on chromosome and the alleles r and s are linked on its homologure, determine the types of gametes that may be fomrred. Include the cross overs and noncross overs.
Press here to check answer. press
Click here to relate meiosis to Sexual Reproduction Strategies
in Humans.
...click here
For information on how to use this page, go to How to Use This Site.
Created by the Center for Learning Technologies, Academic Technology Services.
Last modified October 22, 1997.