
Prophase I -
1. Nuclear membrane pulls
apart and becomes part of the E.R. and the
nucleoli dissolves (disappears).
2. Each DNA molecule
twists and coils back on itself to form rod shaped
chromosomes.
3. Centrioles separate and
a new centriole develops at the base of each
parent centriole forming two centriole organizing centers.
These
centriole organizing centers than migrate to poles on opposite sides
of the
nucleus.
4. Spindle apparatus fill
form from microtubules. Spindles will form between
centromeres
of each chromosome and each centrilole organizing
center,
spindles will form between both centriole organizing
centers,
spindles
will radiate out behind the centrioles and form asters.
5. The chromosomes at this
time are attracted to one another in the following
manner.
Homologous chromosome pairs are attracted to one another. This process is called synapsis and the resulting groups of four chromatids is called tetrads. Locate the three sets of tetrads in the figure below. Draw and label this figure in your notes.

Click here to go back to readings. click
1. The answer is "c". Crossing over can only occur during synapsis when tetrads are formed. Are tetrads formed during mitosis and meiosis II? Check you notes.
Press here to go back to the readings. press
2. The answer is "e". The genes on the same chromatid are linked and
will remain linked unless crossing over occurs.
Press here to go back to the readings. press
3. The answer is "e". Examine the figure below to see how
the genes segregated out during meiosis. Note that only the inside chromatids
crossed over. Write the definition of a chiasma in your notes.
crossing over 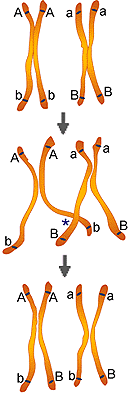
Identify the chiasma in the bottom figure.
Press here to go back to the readings. press
4. The answer is "b". This is very important in understanding the differences between mitosis and meiosis. Review in your notes the drawings of anaphase during these three stages. During mitosis sister chromatids split at the centromere and are pulled to opposite poles, during meiosis I homologous chromosomes are pulled to opposite poles (sister chromatids remain attached) and during meiosis II sister chromatids split at the centromere and are pulled to opposite poles, since this is a mitotic division.
Press here to go back to the readings. press
5. The answers are: Yes, a diploid cell containing 24 chromosomes can undergo mitosis forming two cells each with 24 chromosomes. Yes a diploid cell containing 24 chromosomes can undergo meiosis forming four cells each with 12 chromosomes.
Press here to go back to the readings. press
6. The answers are: Yes, a haploid cell containing
12 chromosomes can undergo mitosis forming two cells each with 12
chromosomes.
Press here to go back to the readings. press
7. The answer is: Yes, a diploid cell containing 24 chromosomes can undergo meiosis forming four cells each with 12 chromosomes.
Press here to go back to the readings. press
8. The answer is: No, a haploid cell containing 12 chromosomes can not undergo meiosis because its chromosome number has already been reduced by one half (contains only one of each homologous pair).
Press here to go back to the readings. press
9. The answer is "b". A diploid cell containing six chromosomes contains three homologous pair.
Press here to go back to the readings. press
10. The answer is "c". The cell contain three sets of two different types of DNA molecules. There are eight ways to arrange these into sets of three DNA molecules per cell.
AaBbCc = one cell before mitosis (diploid)
ABC,
aBC,
AbC,
abC, = 8 cells after meiosis (haploid)
ABc,
aBc,
Abc,
abc,
Press here to go back to the readings. press
10a The four types of gametes are shown in the figure below. The two
top gametes (RS and rs) are the noncross overs and the bottom two
gametes (Rs and rS) are the result of crossing over. ,
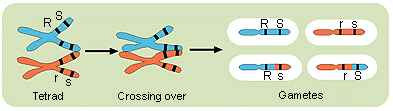
Press here to go back to the readings. press
11. The answer is "a". You may want to look at the figure in your text
showing Chlamydomonas gametes and the human sperm and ovum gametes
Press here to go back to the readings. press
12. The answer is "c".(hint: secondary spermatocyte consists of two
cells; which stage of meiosis consisted of two cells)
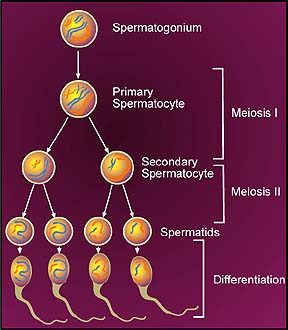
Press here to go back to the readings. press
13. The answer is "b". The spermatid is haploid, therefore only 23 chromosomes.
Press here to go back to the readings. press
14. The answer is "c". Check your figure showing the male reproductive
system.
Press here to go back to the readings. press
15. The answer is "b". Check the chart you made concerning the
male hormones.
Press here to go back to the readings. press
16. The answer is "b". Check you drawing of the human sperm.
Press here to go back to the readings. press
17. The answer is "d". Check you drawing of the human sperm.
Press here to go back to the readings. press
18. The answer is "c". Check the chart you made concerning the
male hormones.
Press here to go back to the readings. press
19. The answer is "c". Study the chart below and identify where the
various stages of meiosis would occur.
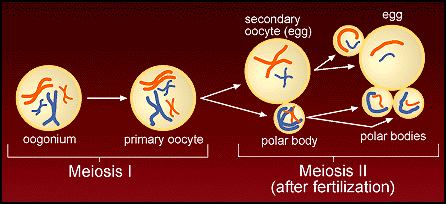
Press here to go back to the readings. press
20. The answer is "b". The ootid is haploid.

Press here to go back to the readings. press
21. The answer is "a". The primary oocyte is diploid.

Press here to go back to the readings. press
22. The correct answer is "a". One egg or ovum and two or three polar bodies.
Press here to go back to the readings. press
23. The answer is "b". Polar bodies are haploid
Press here to go back to the readings. press
24. The answer is "b". Check the table you made concerning female hormones.
Press here to go back to the readings. press
25. The answer is "c". Check the table you made concerning female hormones.
Press here to go back to the readings. press
26.
Press here to go back to the readings. press
27..
Press here to go back to the readings. press
28.
Press here to go back to the readings. press
29.
Press here to go back to the readings. press
30.
Press here to go back to the readings.
For information on how to use this page, go to How
to Use This Site.
Created by the Center for Learning Technologies, Academic Technology Services.
Last modified October 22, 1997.