
Let us now examine the organelles which are found in eukaryotic cells. Even though many of the organelles located in plant cells are the same that are located in animal cells, there are a few organelles not located in both types of cells. These organelles will be indicated when discussing the organelles function. A good way to learn the organelles is to place them in the following groups:
nucleus - structure and function
cytoplasmic organelles - membrane bound, nonmembrane bound
extracellular structures - structure and function
In your notes make an outline with these as your headings.
Read the pages indicated by B-6 and
study behavioral
objectives 7 and 8.
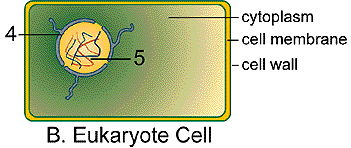
All cells have a nucleus. A few cells are multinucleated (cells
making up the hyphae of fungi) and some cells will lose their nucleus
at maturity (red blood cells). The figure above represents a plant cell
with its nucleus. Note the nuclear membrane indicated by "4". The
nuclear membrane is a double membrane which surrounds the nuclear material
inside of a nucleus called chromatin indicated by "5".
Figure: Eukaryote nucleus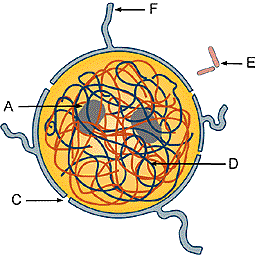
The nucleus (eukaryote nucleus above) is the control center
of the cell. All activities to maintain the cell and to perform a function
for a living organism are controlled by the nucleus. This is accomplished
by the DNA located in the nucleus which directs the syntheses
of specific enzymes (protein) which will perform specific chemical reactions.
This process will be examined in miniunit Delta. The nucleus also controls
cell division. When a cell is stimulated to divide the DNA
will replicate forming two nuclei which directs the cytoplasm to separate
in two parts each containing one of the nuclei. This process will be examined
in miniunit Gamma. In your notes draw a figure similar to the one indicated
by B-8 and write paragraph describing
its function and chemical make up for
the following structures located in the nucleus of a cell: nuclear
membrane (include nuclear pores), chromatin, and nucleoli. Study
behavioral
objective 15.
| Nuclear Membrane | Chromatin | Nucleoli | |
| Chemical Make-up | |||
| Function |

1. Identify "A", "D" and "C" above.
Press here to check for answer. press
When the nucleus of a cell prepares to divide the long slender threads
of DNA (chromatin) will coil and twist back onto itself to form
short thick rod shaped structures called chromosomes. This is a
physical process where the DNA which makes up chromatin takes on a rod
shape form called chromosomes. Examine the figures on the page indicated
by B-8
to compare the differences between chromatin and chromosomes.
Compare these figures with the chromatin/chromosome figure below.
Figure: Chromatin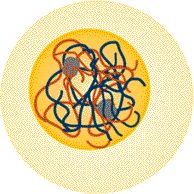 Chromosomes
Chromosomes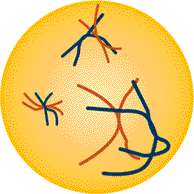
The figure to the lefts shows the DNA molecules in the form of uncoiled,
dispersed chromatin and on the right the DNA molecules have
coiled and condensed to form chromosomes. There are six chromosomes( two
short, two medium and two long length).
In your notes draw a cell containing chromatin and a second cell containing
chromosomes.
2. Which of the following statements does not pertain to the nuclear
membrane.
a) made up of two membrane layers
b) allows for only specific molecules to pass
in and out of the nucleus
c) contains large pores that allow large molecules
pass. through
d) water tight membrane which prevents
chromatin from coming into contact
with the cytoplasm
e) separates the chromatin from the cytoplasm
Press here to check answer. press
3. Which of the following statement does not pertain to the
nucleoli?
a) consists of RNA which will used to form
ribosomes, DNA used to direct the
synthesis of
RNA, protein which may form enzymes that control the
reactions forming
RNA
b) separated from the chromatin by a membrane
c) appears as tightly condensed nucleic acids
and protein
d) main function is to synthesize ribosomes
Press here to check answer. press
4. Which of the following does not pertain to the chromatin?
a) consists of DNA which directs the synthesis
of enzymes that in turn carry out
reactions to
maintain the cell and protein
b) appears as a dark stained mass because
the DNA is a tangle of uncoiled
DNA molecules
c) forms a hollow outer coating which surrounds
the nucleoli
d) separated from the cytoplasm by a double
membrane
Press here to check answer. press
Figure: Nuclear
membrane.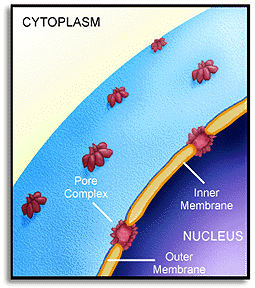
Note: The nuclear membrane in the figure above consists of a double
membrane (inner and outer) and that the pores are coated with protein.
5. What is the function of the pore complex above?
Press here to check answer. press
Nonmembrane organelles can be subdivided into ribosomes and
organelles consisting of protein microtubules or protein filaments.
Ribosomes, like DNA, are present in all
cells. They are located in the cytoplasm of the cell and synthesized in
the nucleoli of the nucleus. Each cell contains millions of ribosomes.
Ribosomes consists of two subunits consisting of RNA (ribosomal RNA) and
protein. Examine the figure of a ribosome indicated by B-7. Draw a ribosome
figure in your notes. Ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis during
which amino acids are condensed (synthesized into) long polymers. This
concept will be explained in miniunit Delta - protein synthesis. Ribosomes
may be found free in the cytoplasm either singly or in groups called
polyribosomes. These free ribosomes synthesize protein which will be used
within the cell. Other ribosomes are attached to endoplasmic reticulum
membranes which
synthesize proteins that may be transported to different places within
the cell or to the outside of a call. Read the pages indicated by B-7
pertaining to ribosomes and write a paragraph comparing the different
types of ribosomes, location of ribosomes, and there function.
Figure: Ribosome 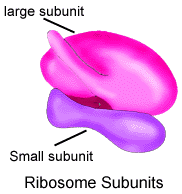
6. The chemical make-up of the structure above is (are) :
a) carbohydrates
d) protein
b) lipids
e) both c and d
c) RNA
Press here to check answer. press
7. Which of the following statements is true.
a) Ribosomes are the site of RNA synthesis
and are synthesized in the
chromatin of the
nucleus.
B) Ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis
and are synthesized in the
cytoplasm.
C) Ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis
and are synthesized in the
nucleolus
D) Ribosomes are site of lipid synthesis and
are synthesized in the nucleolus.
Press here to check answer. press
8. In a working cell protein synthesis occurs:
a) in the nucleus along the outer membrane.
b) in the cytoplasm at the ribosome.
c) in the nucleus at the nucleoli.
d) outside of the cell membrane.
Press here to check answer. press
a) free floating
b) attached to internal membranes
within a cell
c) both a and b
Press here to check answer. press
Read the pages indicated by B-7
pertaining to protein microfilaments and microtubules, study
behavioral objective 10 and write a paragraph comparing the structure
and protein types between these two protein particles.
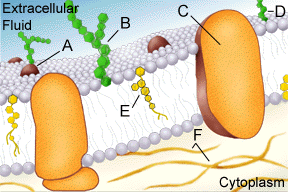
Observe the cytoskeleton labeled "F" above.
A cell's cytoskeleton is made up of both microfilaments and
microtubules. The cytoskeleton gives shape and organization it's
cytoplasm. In your notes write a description of a cytoskeleton explaining
how it shapes and organizes the cytoplasm. The cytoskeleton also aids in
cell movement, organelle movement and cell division. In your notes draw
a cell highlighting the cytoskeleton.
There are several structures in a cell made only of microtubules.
Study behavioral objectives 11,
12 and 13. In your notes compare the microtubular arrangement
of the centriole pair, basal bodies, cilia and flagella.
Draw in your notes, figures representing these four structures and
describe their function and location in a working cell.
Figure: Centriole pair.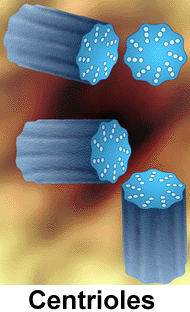
Centriole pairs consist of microtubules in an arrangement of
9(3) +0. Nine sets of three microtubules with none in the center. (See
above) They are always located near the nucleus and are involved
in spindle formation during mitosis and the formation of basal bodies.
Examine figure below to locate in an animal cell (the two solid
rod structures near the nucleus). Centrioles are not found in higher plant
cells. They are always present in animal cells and protista.
Figure: Locate centriole pair .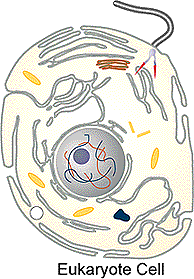
Cilia and flagella are structures which enable cells to move
about or cause currents to move over its surface. Flagella are usually
found in unicellular organisms (Euglena) or structures (sperm) and enables
them to move about. Flagella are usually single or present in low
numbers. Cilia are present in larger numbers. They are used for locomotion
by organisms (paramecium, planarian). They may also beat in a coordinated
manner to force liquid currents to flow over the surfaces of cells.
Flagella are longer than cilia. Both cilia and flagella are formed from
a basal body lying underneath the cell membrane. The basal bodies were
in turned formed by centrioles and migrated to the outer membrane.
Locate the flagella and basal body.
The whip like tail is the flagella. It is long and flexible. The red
structure beneath the cell membrane is the basal body.
These microtubular structures have characteristic microtubular
arrangements. Read the pages and study the figures indicated by B-7
and copy the table below in you notes filling in the correct answers.
(9(3) + 2, 9(2) + 2, 9(3) + 0, 9(3) +1)
| CELL STRUCTURE | MICROTUBULAR ARRANGEMENT |
| centriole | |
| basal body | |
| cilia and flagella |
Learn more concerning the application of these organelles read the pages indicated by B-6 concerning cilia and flagella.
Identify the following statement as pertaining to:
a) centriole
b) basal body c) cilia
d) flagella e) both c and d
10. Structure with 9 + 2 microtubular arrangement
Press here to check answer. press
Identify the following statement as pertaining to:
a) centriole
b) basal body c) cilia
d) flagella e) both c and d
11. Structure with 9 + 0 microtubular arrangement .
Press here to check answer. press
Identify the following statement as pertaining to:
a) centriole
b) basal body c) cilia
d) flagella e) both c and d
12. Structure with 9 + 1 microtubular arrangement
Press here to check answer. press
Identify the following statement as pertaining to:
a) centriole
b) basal body c) cilia
d) flagella e) both c and d
13. Found in pairs (barrel-shaped ring of microtubules) near
the nucleus of animal cells (E - below).

Press here to check answer. press
Identify the following statement as pertaining to:
a) centriole
b) basal body c) cilia
d) flagella e) both c and d
14. Anchored beneath the plasma membrane and give rise to the microtubules
of
the cilia or flagella.
Press here to check answer. press
Identify the following statement as pertaining to:
a) centriole
b) basal body c) cilia
d) flagella e) both c and d
15. Used by single cell organism to move about. These structures are
long and
move in a wavelike motion.
Press here to check answer. press
Identify the following statement as pertaining to:
a) centriole
b) basal body c) cilia
d) flagella e) both c and d
16. Used by a single cell organism to move about. These structures
are short and
move back and forth similar to oars
on a boat.
Press here to check answer. press
Identify the following statement as pertaining to:
a) centriole
b) basal body c) cilia
d) flagella e) both c and d
17. These structures may multiply and move to the underside of the
plasma
membrane forming basal bodies.
Press here to check answer. press
18. Which of the following structures is made up of unit
membrane?
a) mitochondria
d) basal bodies
b) ribosomes
e) flagella
c) centrioles
Press here to check answer. press
This is the end of the third lesson. Click here to go back to
the home page and the fourth lesson Cell Organelles - Membrane Bound.
click
For information on how to use this page, go to How
to Use This Site.
Created by the Center for Learning Technologies, Academic Technology Services.
Last modified October 22, 1997.