
To view a dna molecule.
DNA REPLICATION:
Read the pages indicated by D-12 concerning DNA replication. Study behavioral objectives 29-31.
OVERVIEW:
Recall that DNA is double stranded, twisted in the form of a helix. The two DNA strands of each double helix unwinds. One side of the double strand will uncouple from the opposite strand (unzips). While these two strands are apart individual nucleotides will match up to complementary partners. With the aid of an enzyme DNA polymerase, which moves along each strand of the nucleotides, will hook together by condensation. You learned the condensation reaction in an earlier miniunit.
END RESULT:
After replication two double helices are synthesize, each consisting of one parental DNA strand plus one newly synthesized complementary strand. the new strand is an exact copy of the other parental strand. The two daughter DNA molecules are therefore duplicates of the parental DNA molecule.
After reading the pages in the text write out a step by step description
of events which led to the synthesis of a DNA molecule. Include the
following terms:
helicies, polymerases, semiconservative replication and 3' to
5' direction.
1. Click here to check answer.
2. Semiconservative replication refers to the fact that:
a) only certain bases pair to specific bases
b) one DNA strand remains while the other is newly
synthesized
c) only the newly synthesized DNA contains genes
d) both DNA strands contain newly synthesized nucleotides
Click here to check answer.
3. DNA ligase:
a. connects backbones of newly synthesized polynucleotide.
b. initiates the unwinding of a double helix.
c. directs free nucleotides to exposed bases.
Click here to check answer.
4. If the bases in the parent DNA strand are AATCATGGC what would be the correct base sequence located in the complimentary strand.
Click here to check answer.
When does replication occur in a working cell? This is the process
which occurs during the "S" stage of cell division. You may want to go
back and review that part of mitosis and meiosis.
TRANSCRIPTION:
Read pages indicated by D-13
and study behavioral
objectives 28, 32, 35, and 36.
OVERVIEW:
During transcription DNA will synthesize RNA. Three types of RNA will
be synthesized: mRNA (messenger), tRNA (tranasfer) and rRNA (ribosomal).
During the transcription of mRNA the information contained in a DNA segment
(gene) is copied into a mRNA strand. This process is similar to DNA replication
except only a small segment of DNA is copied, and the nucleotides
which are bonded are the ones which make up RNA. Recall from the previous
lesson that RNA nucleotides consist of the sugar ribose in place
of deoxyribose, and the base A,U,C,G in place of A,T,C,G.
END RESULTS: Only one strand of the double stranded DNA
forms a complimentary strand of mRNA. This RNA represents only
a small portion of the entire DNA (gene). It contains the sugar ribose
in place of deoxyribose and the same bases as the DNA parent strand except
"U" in the place of "T".
5. After reading the pages in the text write out a step by
step description of events which lead to the synthesis of a mRNA molecule.
Include the following processes: section of DNA transcribed, template strand,
RNA polymerse, promoter, initiation, elongation of RNA molecule, and termination.
Click here to check answer.
6. If the bases on the template DNA strand for a gene are TTTAATCATGGC, what would be the correct base sequence of the mRNA synthesized by transcription?
Click here to check answer.
The tRNA and the rRNA are transcribed in a similar manner. The genes which code for the synthesis of rRNA are located in the nucleolus and the genes which code for the synthesis of tRNA are located in chromatin DNA.
All three of these RNA's are transcribed in the nucleus and must move
into the cytoplasm where they will coordinate the efforts which
will lead to the synthesis of a specific protein directed by the mRNA.
These are very large molecules and will move into the cytoplasm though
the nuclear pores.
TRANSLATION:
Study behavioral objectives 33, 34 and 37 and read the pages indicated by D-14
Translation is the synthesis of a protein which is directed by a code
inscribed on the mRNA molecule. Translation occurs on the ribosome
in the cytoplasm and requires the use of the three RNA's: mRNA, tRNA and
rRNA (see B.O. 32).
OVERVIEW:
Only the mRNA carries the code from the gene to synthesize a specific protein. During the process ribosome's (made up of protein and rRNA) act as a stage for the following specific events: tRNA picks up specific amino acids located in the cytoplasm and transfers them to the ribosome, mRNA contains the code which is decoded by the tRNA and places specific amino acids in close proximity in order for them to bond together by condensation to form a protein.
Fill out the following table and place in you notes.
| ////////// | function during translation | codon present (yes or no) | anticodon present (yes or no) | where synthesized |
| mRNA |
|
|||
| tRNA |
|
|||
| rRNA |
|
END RESULTS:
A protein with a specific primary structure will be formed. The specific primary structure is directed by the gene (DNA segment) which was transcribed to a mRNA.
After reading the pages in the text, write out a step by step description of events which occurs during translation. Include the following processes: location of mRNA and tRNA on the ribosome, initiator tRNA, codon, anticodon, protein elongation, stop codons.
SUMMARY OF EVENTS:
mRNA with code for amino acid sequences of protein attaches to the ribosome.
Ribosome's consist of rRNA and protein. They bind with the mRNA and part of the tRNA with corresponding amino acids.
tRNA consist of three exposed nitrogen bases (anticodons) at one end and a specific amino acid at the opposite end.
As the mRNA slides along the ribosome specific tRNA, they (anticodon) match up to the mRNA (codons) exposed on the ribosome.
Example:
mRNA with the base sequences "AUGAAACCC" represents three codons and
would match up with three tRNA with the following anticodons - UAC, UUU,
GGG.
The amino acids carried to the ribosome by tRNA will be linked together by condensation reactions learned in an earlier unit.
The first initiator tRNA "UAC" will move from the cytoplasm to the AUG codon of the mRNA which has positioned itself on the ribosome. The second tRNA "UUU" with its corresponding amino acid will move from the cytoplasm to the "AAA" codon of the ribosome. The two amino acids will link together by condensation reaction. The first initiator tRNA will break away from the DNA leaving its amino acid attached to the second amino acid still attached to the tRNA with the "UUU" anticodon.
As the mRNA moves along the ribosome a third tRNA "GGG" with its amino acid attaches to the DNA by the anticodon/codon attraction.
This amino acid will linked to the end of the dipeptide present and the second tRNA will move from the parent DNA
These steps are repeated over and over until a codon with a STOP
message appears.
The STOP messages ends the synthesis of the polypeptide.
Because the codons are in triplets there are 64 different combinations of anticodon and codon. There are approximately 20 amino acids. Therefore, some of the amino acids may be associated with tRNAs with different anticodon..
Study the Genetic Code (codons of mRNA) table below. Learn to read
this table. Note that the triplets refer to the codons on the
mRNA and not the anticodons of the tRNA.
codon table 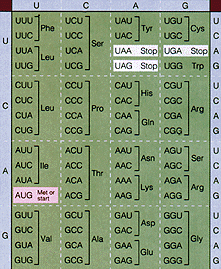
7. Which RNA contains codons?
Click here to check answer.
8. Which RNA contains anticodons?
Click here to check answer.
9. How many bases are in a codon or anticodon?
Click here to check answer.
10. What is the codon for the initiator tRNA?
Click here to check answer.
11. If a gene had the following base sequence TACCCTCAAGATGCGTTC,
what would be the sequence of bases on the mRNA?
Click here to check answer.
12. Which RNA's would be used to bring the specific amino acids to the ribosome? Remember this table represents the codon and not the anticodon.
Click here to check answer.
13. Using the Genetic Code table determine the primary structure of
the protein formed (sequence of amino acids)?
codon table
Click here to check answer.
14. What would be the base sequence for the gene which forms the following
polypeptide (include start and stop)?
methionine-tyrosine-lysine-phenyalanine-phenylalanine-cysteine-glycine-lysine
codon table 
Click here to check answer.
15. Identify the amino acids which is associated with the anticodon
UUU.

Click here to check answer.
16. Identify the amino acid which is associated with the codon AAC.
codon
Click here to check answer.
Study behavioral objectives 25. A specific protein (sequence of amino acids) is formed during translation. The orderly sequence of amino acids were directed by a segment of DNA (gene). The DNA formed a complementary mRNA during transcription. The mRNA's arrangement of nitrogen bases (codons) attracted specific tRNA due to their anticodons during translation. The protein formed takes on a particular three dimensional shape depending on its primary structure which dictates proteins secondary structure, tertiary structure and quaternary structure if present. At this point the protein is called an enzyme. This enzyme will in turn catalyze a specific reaction causing a particular phenotype, such as red flower color.
Relate the paragraph above to the figure below.
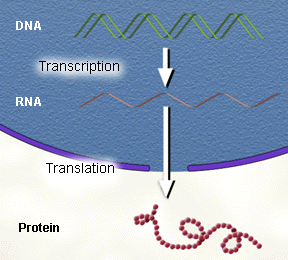
Write the function for the following terms as to their roll in translation.
RNA polymerase -
promoter region of gene -
start codon -
stop codon -
MUTATIONS
Study behavioral objective 24 and read the section indicated by D-16.
204-207 in the text.
In your notes write a paragraph contrasting between point mutations, insertion mutations and deletion mutations.
Write a paragraph explaining the effect of mutations on protein structure and function.
In summary, how do genes work in producing the various phenotypes which make up all living organisms, bacteria, plants and animal? Study the following statements and write in your notes.
Let's work backwards starting with the specific phenotype. For example, what causes some individuals to have facial freckles? This phenotype is caused by specific chemical reactions that occur in some of the epidermal cell of that individual. During this process the pigment melin is synthesized.
Protein Synthesis
What controls these reactions? In an earlier miniunit you learned that chemical reactions in living cells are controlled by enzymes. Also you learned that enzymes are made up of protein and have specific three dimension structure dictated by their primary structure (sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide).
How are these specific polypeptide (protein) synthesized? Proteins
are synthesized at the ribosome's in the cytoplasm during the process of
translation.
Translation is where a specific mRNA (contains a specific arrangements
of nucleotides) are decoded by a tRNA. The tRNA molecule has specific
amino acids attached at one end in relation the the anticodon
(triplet bases) at a different location. These anticodons match up with
triplet codons located on the mRNA. Therefore the codons on the
mRNA are directing the synthesis of a specific protein. Where did
mRNA receive this message (arrangement of nucleotides forming the triplet
codon)? The mRNA was copied from a small segment of DNA (gene)
during the process of transcription.
This is the end of miniunit Delta. Go back to the home
page and examine the www pages concerning miniunit Delta. They may be found
in the resource section. You may now take the practice test for miniunit
Delta. Click here to go back to the Biology 108N home page and review or
take the practice test. Good Luck!
Please return to the home front page
.
For information on how to use this page, go to How
to Use This Site.
Created by the Center for Learning Technologies, Academic Technology Services.
Last modified October 22, 1997.